Corpus: Mylohyoid muscle: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
K (F3747F4152546 verschob die Seite Corpus:Mylohyiod muscle nach Corpus:Mylohyoid muscle, ohne dabei eine Weiterleitung anzulegen) |
Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
||
| (Eine dazwischenliegende Version von einem anderen Benutzer wird nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
''from ancient Greek: μύλη ("myle") - millstone, mill tooth; ὑοειδής ("hyoides") - υ-shaped'' | |||
== Definition == | |||
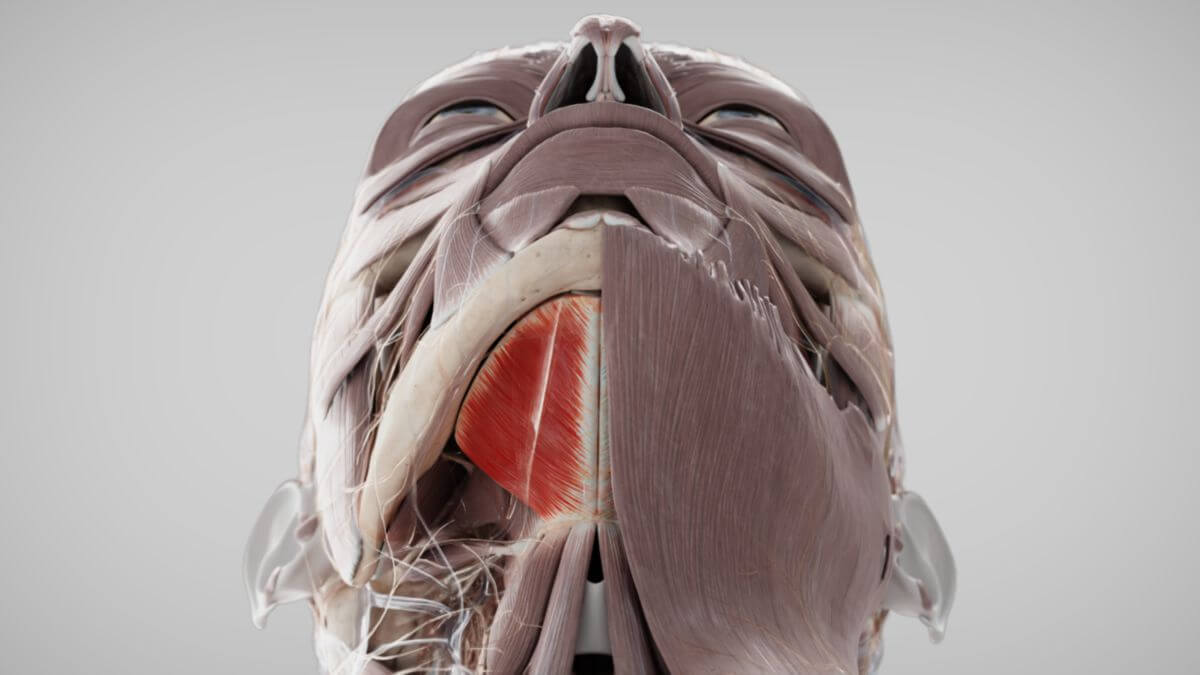
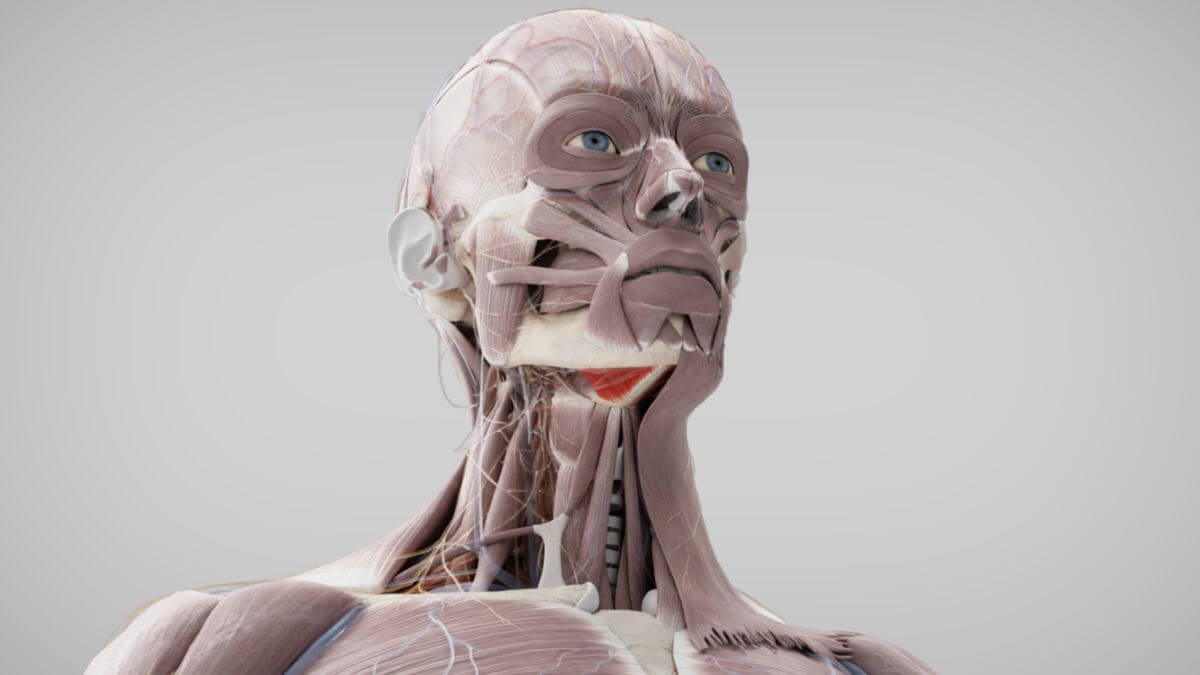
The '''mylohyoid muscle''' is a [[Corpus:skeletal muscle|skeletal muscle]] that is part of the [[Corpus:Suprahyoid musculature|suprahyoid musculature]], forming the muscular foundation of the [[Corpus:floor of the mouth|floor of the mouth]]. It is derived from the first branchial arch.<dcembed ratio="16x9"><dcEmbedUrl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/photos/43058-musculus-mylohyoideus"></dcEmbedUrl> | |||
==Definition== | |||
The '''mylohyoid muscle''' is a skeletal muscle | |||
<dcEmbedUrl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/photos/43057-musculus-mylohyoideus"></dcEmbedUrl></dcembed> | <dcEmbedUrl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/photos/43057-musculus-mylohyoideus"></dcEmbedUrl></dcembed> | ||
==Course== | ==Course== | ||
The | The mylohyoid muscle originates from the [[Corpus:Mylohyoid line|mylohyoid line]] (linea mylohyoidea) on the inner surface of the [[Corpus:Mandible|mandible]]. From its origin, the muscle fibers run downward towards the [[Corpus:Hyoid bone|hyoid bone]]. The posterior fibers of the mylohyoid muscle attach directly to the hyoid bone, while the anterior fibers converge with those from the opposite side at the midline connective tissue structure called the [[Corpus:Mylohyoid raphe|mylohyoid raphe]], which extends from the [[Corpus:Chin|chin]] to the hyoid bone.<dcembed><dcembedurlskatchfab src="https://sketchfab.com/3d-models/54d5f07def0b4db882d0f971d39cfb6a" ui_controls="1"></dcembedurlskatchfab></dcembed> | ||
The posterior | |||
<dcembed><dcembedurlskatchfab src="https://sketchfab.com/3d-models/54d5f07def0b4db882d0f971d39cfb6a" ui_controls="1"></dcembedurlskatchfab></dcembed> | |||
==Innervation== | ==Innervation== | ||
The mylohyoid muscle is innervated by the [[Corpus:Mylohyoid nerve|mylohyoid nerve]], a branch of the [[Corpus:Inferior alveolar nerve|inferior alveolar nerve]], which is itself a branch of the [[Corpus:Mandibular nerve|mandibular nerve]] (cranial nerve V3). | |||
==Vascular supply== | ==Vascular supply== | ||
The muscle | The muscle receives its blood supply from the mylohyoid branch of the [[Corpus:Inferior alveolar artery|inferior alveolar artery]]. | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
The mylohyoid muscle | The mylohyoid muscle plays a key role in the swallowing process by pulling the hyoid bone anteriorly. It also contributes to jaw opening and assists in the grinding movement of the [[Corpus:Jaw|jaw]]. As a broad muscle, the mylohyoid forms the muscular floor of the mouth, also known as the [[Corpus:Diaphragm oris|diaphragm oris]]. | ||
<dcembed ratio="16x9"><dcembedurl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/videos/3578-musculus-mylohyoideus"></dcembedurl></dcembed> | <dcembed ratio="16x9"><dcembedurl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/videos/3578-musculus-mylohyoideus"></dcembedurl></dcembed> | ||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
The term | The term "mylohyoid muscle" reflects its anatomical course, indicating both its origin and insertion points. The muscle originates from the mandible in the area of the [[Corpus:Molar (tooth)|molars]] (derived from the ancient Greek word "mylai" meaning molars) and extends to the hyoid bone (os hyoideum). | ||
[[Kategorie:Corpus]] | [[Kategorie:Corpus]] | ||
[[Kategorie:Head]] | [[Kategorie:Head]] | ||
[[Kategorie:Muscle]] | [[Kategorie:Muscle]] | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 17. Oktober 2024, 10:36 Uhr
from ancient Greek: μύλη ("myle") - millstone, mill tooth; ὑοειδής ("hyoides") - υ-shaped
Definition
The mylohyoid muscle is a skeletal muscle that is part of the suprahyoid musculature, forming the muscular foundation of the floor of the mouth. It is derived from the first branchial arch.
Course
The mylohyoid muscle originates from the mylohyoid line (linea mylohyoidea) on the inner surface of the mandible. From its origin, the muscle fibers run downward towards the hyoid bone. The posterior fibers of the mylohyoid muscle attach directly to the hyoid bone, while the anterior fibers converge with those from the opposite side at the midline connective tissue structure called the mylohyoid raphe, which extends from the chin to the hyoid bone.
Innervation
The mylohyoid muscle is innervated by the mylohyoid nerve, a branch of the inferior alveolar nerve, which is itself a branch of the mandibular nerve (cranial nerve V3).
Vascular supply
The muscle receives its blood supply from the mylohyoid branch of the inferior alveolar artery.
Function
The mylohyoid muscle plays a key role in the swallowing process by pulling the hyoid bone anteriorly. It also contributes to jaw opening and assists in the grinding movement of the jaw. As a broad muscle, the mylohyoid forms the muscular floor of the mouth, also known as the diaphragm oris.
Etymology
The term "mylohyoid muscle" reflects its anatomical course, indicating both its origin and insertion points. The muscle originates from the mandible in the area of the molars (derived from the ancient Greek word "mylai" meaning molars) and extends to the hyoid bone (os hyoideum).