Guanosinmonophosphat
Synonyme: GMP, Guanylsäure
Englisch: guanosine monophosphate, guanylate
Definition
Als Guanosinmonophosphat oder Guanylat bezeichnet man das Monophosphat des Guanins. Es gehört zur Gruppe der Nukleotide.
Biochemie
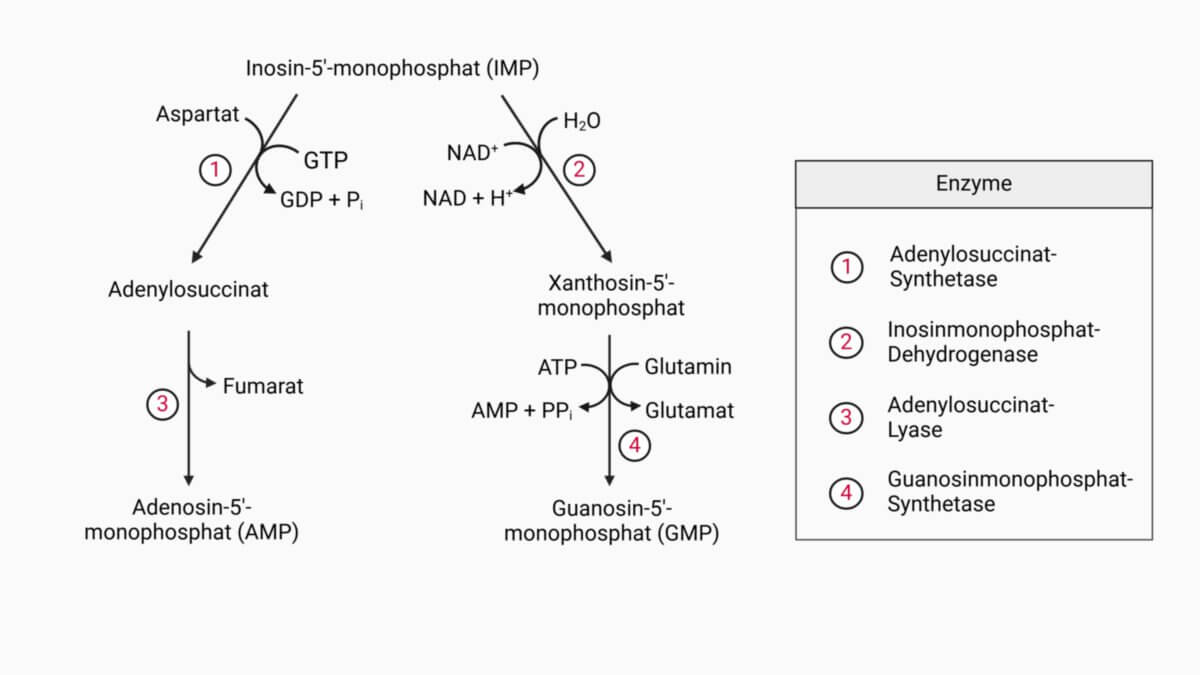
Guanosinmonophosphat wird de novo aus Inosinmonophosphat (IMP) synthetisiert. Dabei wird im ersten Schritt IMP mithilfe der Inosinmonophosphat-Dehydrogenase zu Xanthosin-5'-monophosphat oxidiert. Im nächsten Schritt ersetzt die GMP-Synthase unter ATP-Verbrauch das zuvor eingeführte Sauerstoffatom durch eine Aminogruppe und bildet so Guanosinmonophosphat. Als Donor agiert dabei Glutamin, das durch die Katalyse zu Glutamat umgewandelt wird.
Darüber hinaus entsteht Guanosinmonophosphat beispielsweise bei der Abspaltung von Pyrophosphat von GTP oder beim Abbau der DNA und kann unter Verbrauch anderer Nukleosidtriphosphate wieder zu GTP phosphoryliert werden.
Ist der Phosphatrest an Desoxyribose gebunden, spricht man von Desoxyguanosinmonophosphat bzw. Desoxyguanylat (dGMP).
GMP kommt in zyklischer Form als cGMP vor, das eine wichtige Rolle als Second Messenger spielt.