Corpus: Supinator muscle
1. Definition
2. Anatomy
2.1. Origin
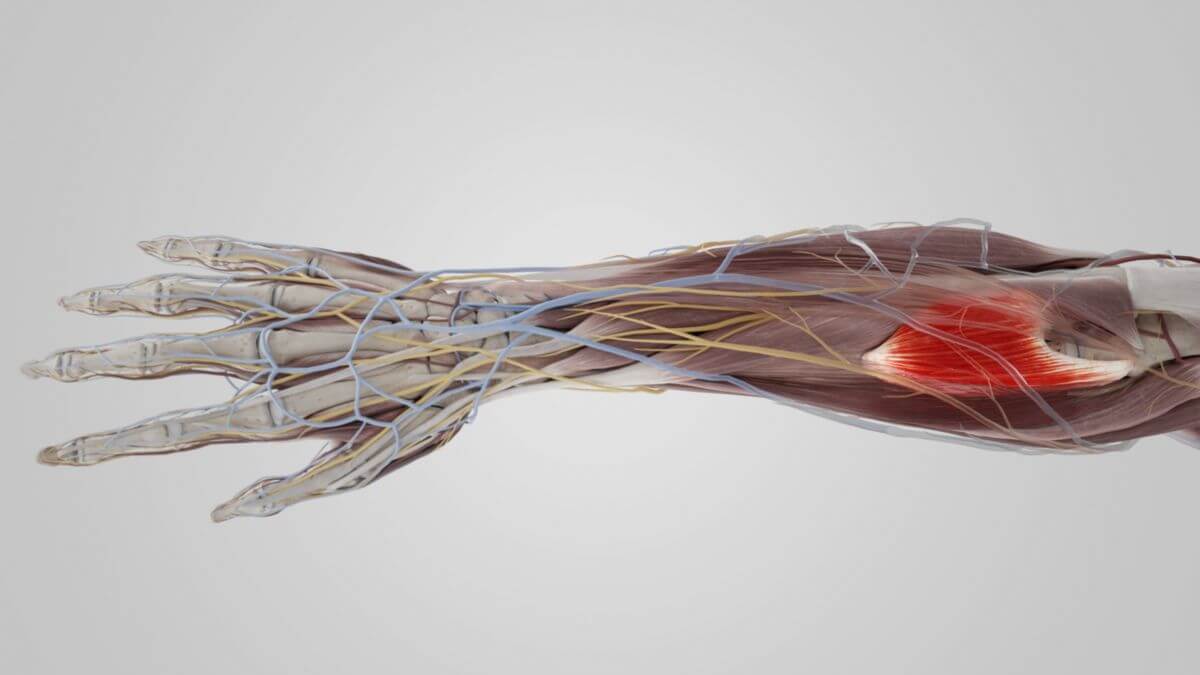
The supinator muscle originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, the radial collateral ligament of the elbow joint (Ligamentum collaterale radiale), and the annular ligament. Additional fibers originate from a small bony prominence of the ulna (Crista musculi supinatoris).
The muscle wraps around the upper third of the radius and consists of two layers of fibers, between which the deep branch of the radial nerve can be found.
2.2. Insertion
The insertion of the supinator muscle is in the upper third of the radius, encircling the anterior, lateral, and posterior surface of the bone up to the insertion of the pronator teres muscle.
3. Innervation
The innervation of the supinator muscle is provided by the deep branch of the radial nerve from the brachial plexus (segments: C5 and C6).
Since the deep branch of the radial nerve pierces the supinator muscle, it is easily located and serves as a key landmark for the nerve.
4. Function
As its name suggests, the supinator muscle is responsible for the supination of the forearm.