Corpus: Multifidi muscles: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(Englische Seite angelegt) |
KKeine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
||
| (Eine dazwischenliegende Version von einem anderen Benutzer wird nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
==Definition== | ==Definition== | ||
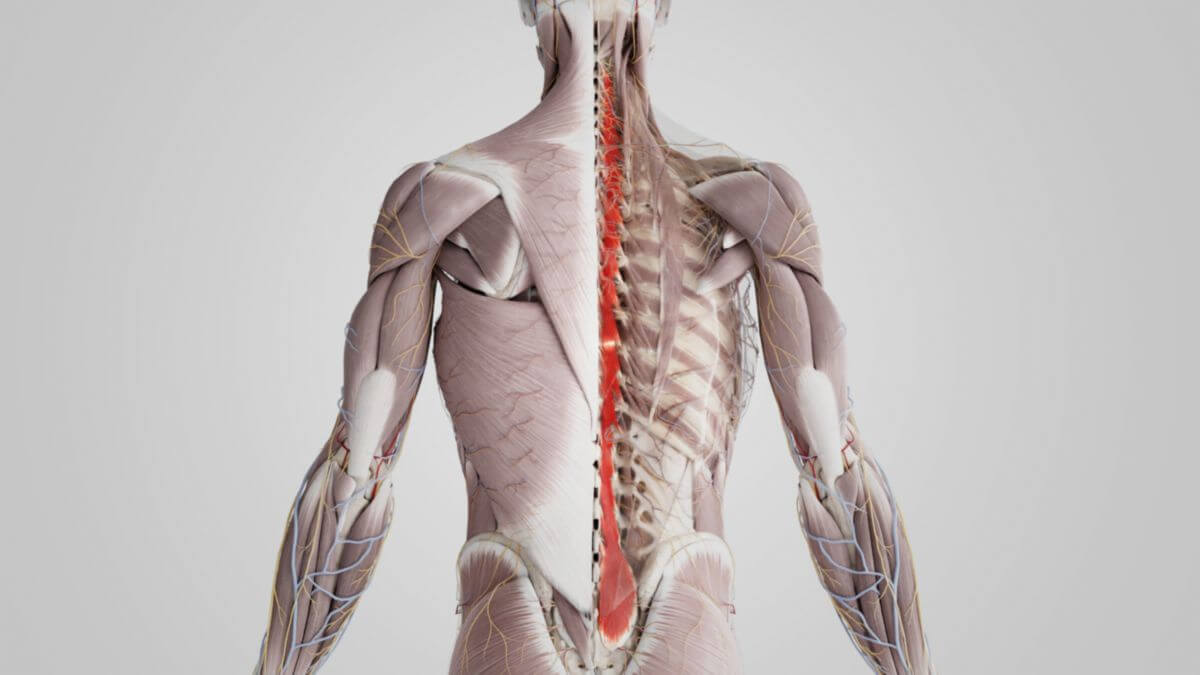
The ''' | The '''multifidi''' '''muscles''' are [[Corpus:Skeletal muscle|skeletal muscles]] that are part of the [[Corpus:Muscle|back musculature]]. They belong to the medial tract of the [[Corpus:Erector spinae muscle group|erector spinae muscle group]].<dcembed ratio="16x9"><dcEmbedUrl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/photos/42910-musculus-multifidus"></dcEmbedUrl></dcembed> | ||
==Course== | ==Course== | ||
The multifidi muscles extend from the [[Corpus:Transverse processes|transverse processes]] in the [[Corpus:Thoracic spine|thoracic spine]] to the [[Corpus:Spinous processes|spinous processes]] of the higher [[Corpus:Vertebra|vertebrae]]. In the [[Corpus:Cervical spine|cervical spine]], they originate from the superior articular processes, while in the [[Corpus:Lumbar spine|lumbar spine]], they originate from the mammillary processes. The areas of origin also extend to neighboring vertebral bodies, and in the caudal region, they attach to the [[Corpus:Sacrum|sacrum]], the [[Corpus:Posterior sacroiliac ligament|posterior sacroiliac ligament]], and the [[Corpus:Iliac crest|iliac crest]]. | The multifidi muscles extend from the [[Corpus:Transverse processes|transverse processes]] in the [[Corpus:Thoracic spine|thoracic spine]] to the [[Corpus:Spinous processes|spinous processes]] of the higher [[Corpus:Vertebra|vertebrae]]. In the [[Corpus:Cervical spine|cervical spine]], they originate from the superior articular processes, while in the [[Corpus:Lumbar spine|lumbar spine]], they originate from the mammillary processes. The areas of origin also extend to neighboring vertebral bodies, and in the caudal region, they attach to the [[Corpus:Sacrum|sacrum]], the [[Corpus:Posterior sacroiliac ligament|posterior sacroiliac ligament]], and the [[Corpus:Iliac crest|iliac crest]]. | ||
The deeper fibers of the multifidi skip two vertebrae, while the superficial fibers can skip up to five vertebral levels. The multifidi muscles extend caudally to the sacrum and attach cranially to the caudal surface of the second [[Corpus:Cervical vertebra|cervical vertebra]].<dcembed><dcembedurlskatchfab src="https://sketchfab.com/3d-models/6528344795a94fe389b15a90a0a4d8ac" ui_controls="1"></dcembedurlskatchfab></dcembed> | The deeper fibers of the multifidi muscles skip two vertebrae, while the superficial fibers can skip up to five vertebral levels. The multifidi muscles extend caudally to the sacrum and attach cranially to the caudal surface of the second [[Corpus:Cervical vertebra|cervical vertebra]].<dcembed><dcembedurlskatchfab src="https://sketchfab.com/3d-models/6528344795a94fe389b15a90a0a4d8ac" ui_controls="1"></dcembedurlskatchfab></dcembed> | ||
==Innervation== | ==Innervation== | ||
The multifidi muscles are innervated by the medial branches of the posterior | The multifidi muscles are innervated by the medial branches of the posterior branch from the respective segmental [[Corpus:Spinal nerve|spinal nerves]]. | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 21. August 2024, 13:26 Uhr
Definition
The multifidi muscles are skeletal muscles that are part of the back musculature. They belong to the medial tract of the erector spinae muscle group.
Course
The multifidi muscles extend from the transverse processes in the thoracic spine to the spinous processes of the higher vertebrae. In the cervical spine, they originate from the superior articular processes, while in the lumbar spine, they originate from the mammillary processes. The areas of origin also extend to neighboring vertebral bodies, and in the caudal region, they attach to the sacrum, the posterior sacroiliac ligament, and the iliac crest.
The deeper fibers of the multifidi muscles skip two vertebrae, while the superficial fibers can skip up to five vertebral levels. The multifidi muscles extend caudally to the sacrum and attach cranially to the caudal surface of the second cervical vertebra.
Innervation
The multifidi muscles are innervated by the medial branches of the posterior branch from the respective segmental spinal nerves.
Function
The multifidi muscles have different functions depending on how they contract. When they contract unilaterally, they rotate the spine to the opposite side and cause lateral flexion to the same side. Bilateral contraction of the multifidi muscles results in the extension of the relevant section of the spinal column.
Clinic
Targeted training of the multifidi muscles, particularly through physiotherapy, is crucial after surgical interventions for herniated discs. Strengthening these muscles is essential for regaining and improving the stability of the affected spinal segments.