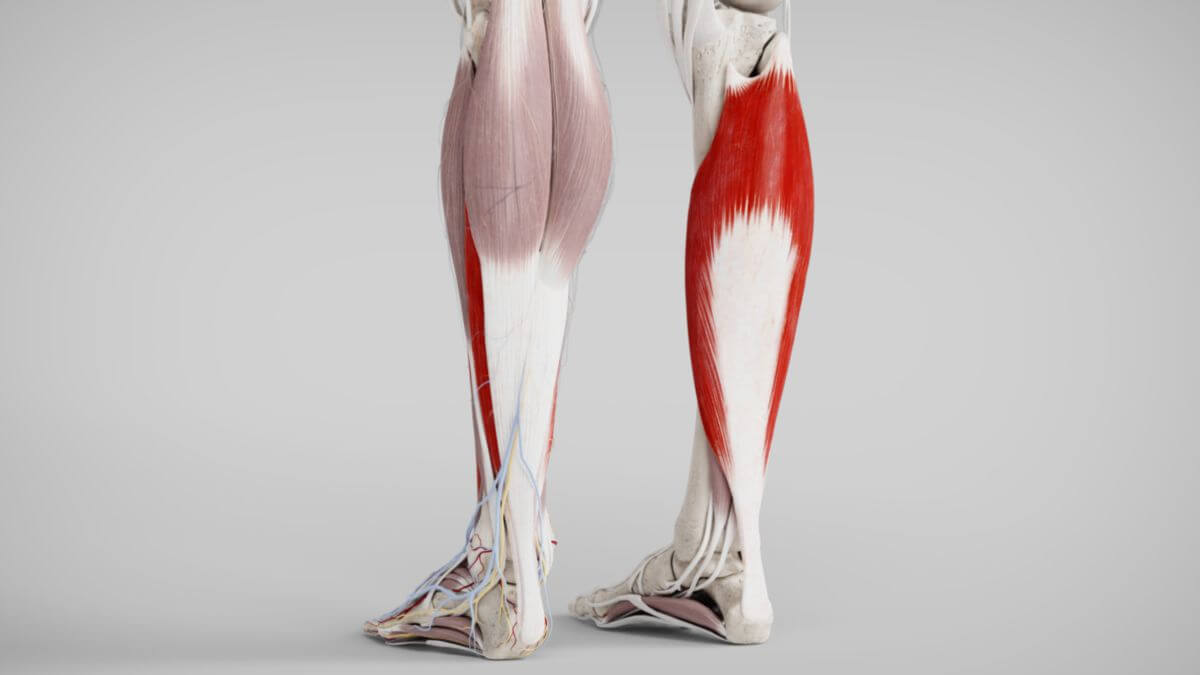
Corpus: Soleus muscle
1. Definition
The soleus muscle is a skeletal muscle that is part of the lower leg muscles. It interacts with the gastrocnemius muscle, and together, they are often referred to in anatomical literature as the triceps surae muscle.
2. Anatomy
The soleus muscle is a multi-pinnate muscle that typically has a separate aponeurosis from the gastrocnemius muscle.
2.1. Course
The soleus muscle originates from the head and the upper third of the dorsal surfaces of the fibula and tibia. The space between these origins is bridged by a tendinous arch. This tendinous edge forms a passage for the popliteal artery and vein, as well as the tibial nerve.
The muscle belly is visible under the lateral edges of the gastrocnemius muscle. The end tendons of both muscles join to comprise the Achilles tendon, which attaches to the lower edge of the calcaneal tuberosity.
2.2. Innervation
The soleus muscle is innervated by the tibial nerve, which originates from the sciatic nerve (segments S1 and S2).
3. Function
The soleus muscle is responsible for plantar flexion and supination of the foot. It prevents the lower leg from bending forwards at the talocrural joint, thereby securing the stance.