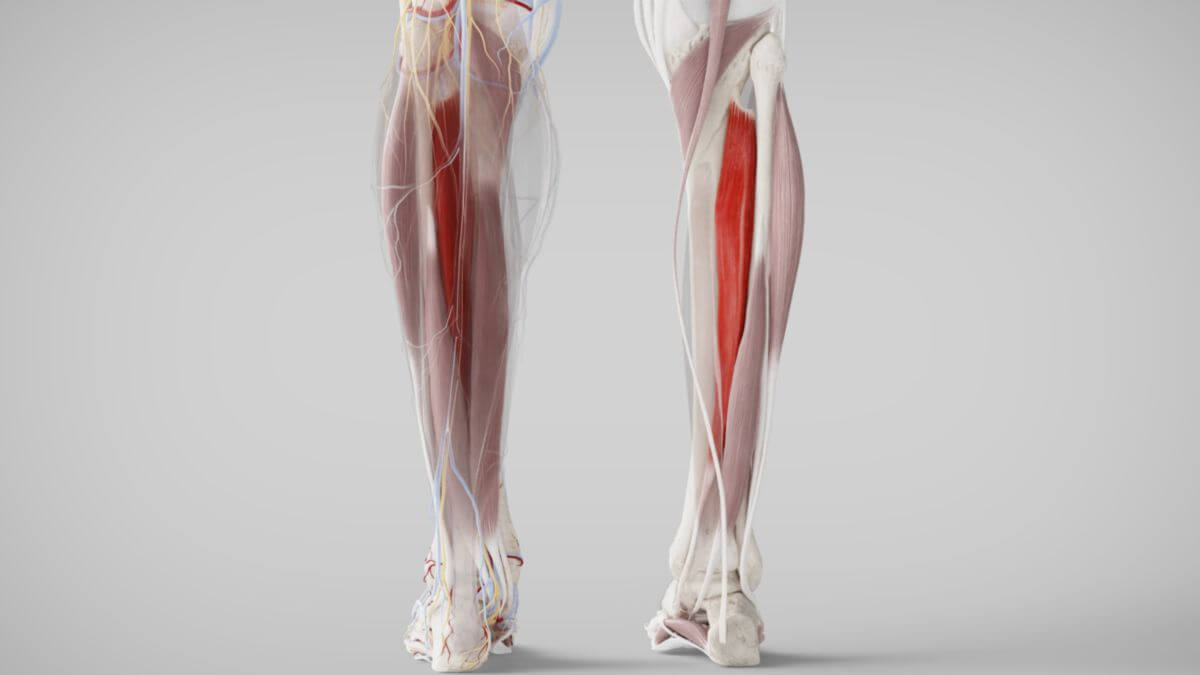
Corpus: Tibialis posterior muscle
Synonym: posterior tibial muscle
1. Definition
The posterior tibialis muscle is a skeletal muscle from the lower leg muscle group that belongs to the deep calf muscles.
2. Course
The primary origin of the posterior tibialis muscle is the posterior surface of the interosseous membrane. Additionally, it originates from the adjacent surfaces of the tibia and fibula, as well as the deep layer of the fascia cruris, which separates the flexor muscles.
In the lower leg, the tendon of the posterior tibialis muscle passes beneath the tendon of the flexor digitorum longus muscle, forming the crural chiasm. The tendon then diverges to multiple attachment points.
The main attachment point is the tuberosity of the navicular bone. Other fibers of the tendon attach to the medial cuneiform bone and the bases of the second to fourth metatarsal bones.
3. Innervation
The posterior tibial muscle is innervated by the tibial nerve.
4. Function
When contracted, the posterior tibialis muscle causes supination and adduction of the foot and is involved in plantar flexion. Along with the tendon of the fibularis longus muscle and the transverse head of the adductor hallucis muscle, it plays a crucial role in stabilizing the physiological transverse arch of the foot skeleton.
5. Clinic
Degenerative changes in the tendon of the posterior tibialis muscle can lead to tibialis posterior syndrome (PTTD).