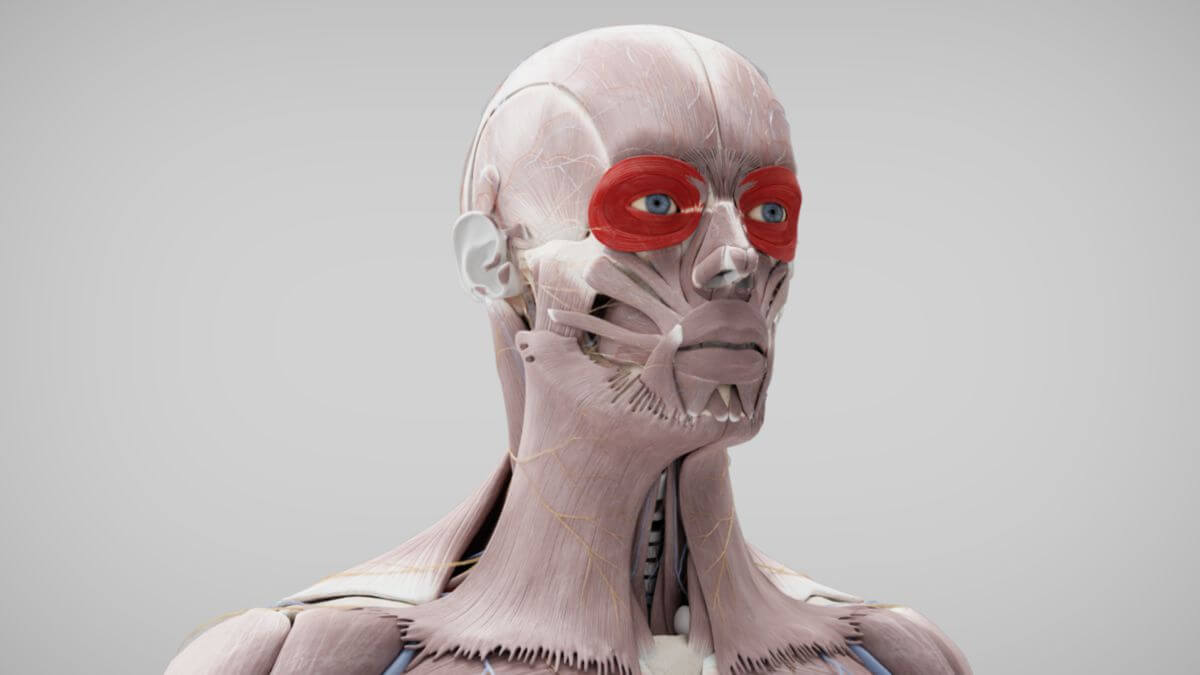
Corpus: Orbicularis oculi muscle
from Latin: orbis - circle, disc; oculus - eye
1. Definition
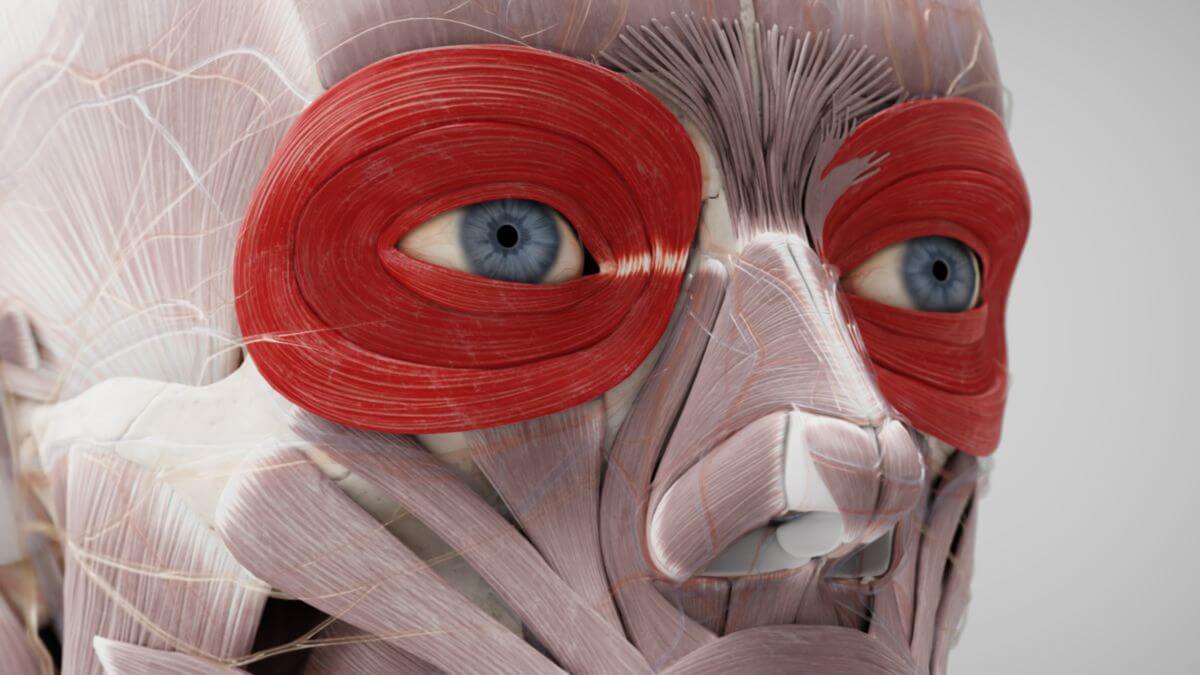
The orbicularis oculi muscle is a muscle that encircles the eye, surrounding the orbital opening (aditus orbitalis) and enclosing the palpebral fissure. It is part of the facial expression (mimic) musculature.
2. Course
The orbicularis oculi muscle is composed of three distinct parts:
- Orbital part (Pars orbitalis): This part originates from the frontal process of the maxilla and the nasal part of the frontal bone. It surrounds the palpebral fissure like a sphincter.
- Palpebral part (Pars palpebralis): It originates from the medial palpebral ligament and attaches to the lateral palpebral raphe.
- Lacrimal part (Pars lacrimalis): This part originates from the posterior lacrimal crest and surrounds the lacrimal sac.
3. Innervation
The orbicularis oculi muscle is innervated by the temporal and zygomatic branches of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII).
4. Blood supply
The muscle receives its blood supply from the zygomaticoorbital branch of the superficial temporal artery.
5. Function
The primary function of the orbicularis oculi muscle is to close the eyelids. Additionally, it plays a role in:
- Distributing tear fluid (tear film)
- Facilitating tear drainage
Because the muscle is fused with the underlying skin, its contractions result in the skin following its movements. The skin folds that form at the lateral edge of the eye during contraction are commonly referred to as "crow's feet."
6. Clinic
In cases of facial nerve palsy, where the muscle fails to close the eyelid, the physiological upward movement of the eyeball becomes visible, a phenomenon known as the Bell's phenomenon. Additionally, there may be an outward turning of the lower eyelid, a condition called paralytic ectropion (ectropion paralyticum).
Tapping on the lateral canthus or the glabella can trigger the eyelid closure reflex, resulting in a contraction of the orbicularis oculi muscle.
In aesthetic medicine, the "crow's feet" caused by the orbicularis oculi muscle can be smoothed out with localized injections of botulinum toxin A.