Corpus: Subclavius muscle: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
K (Schützte „Corpus:Subclavius muscle“ ([Bearbeiten=Nur Administratoren erlauben] (unbeschränkt) [Verschieben=Nur Administratoren erlauben] (unbeschränkt))) |
Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung Markierung: 2017-Quelltext-Bearbeitung |
||
| (2 dazwischenliegende Versionen von 2 Benutzern werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
''from Latin: clavus - nail'' | ''from Latin: clavus - nail'' | ||
==Definition== | ==Definition== | ||
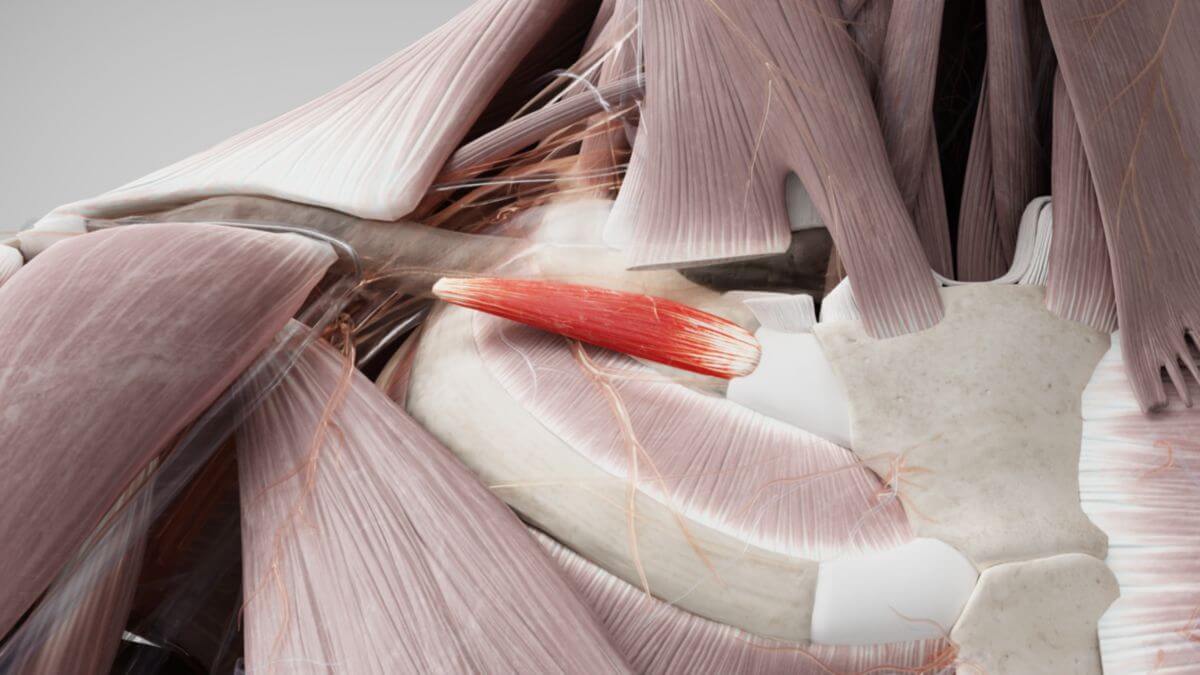
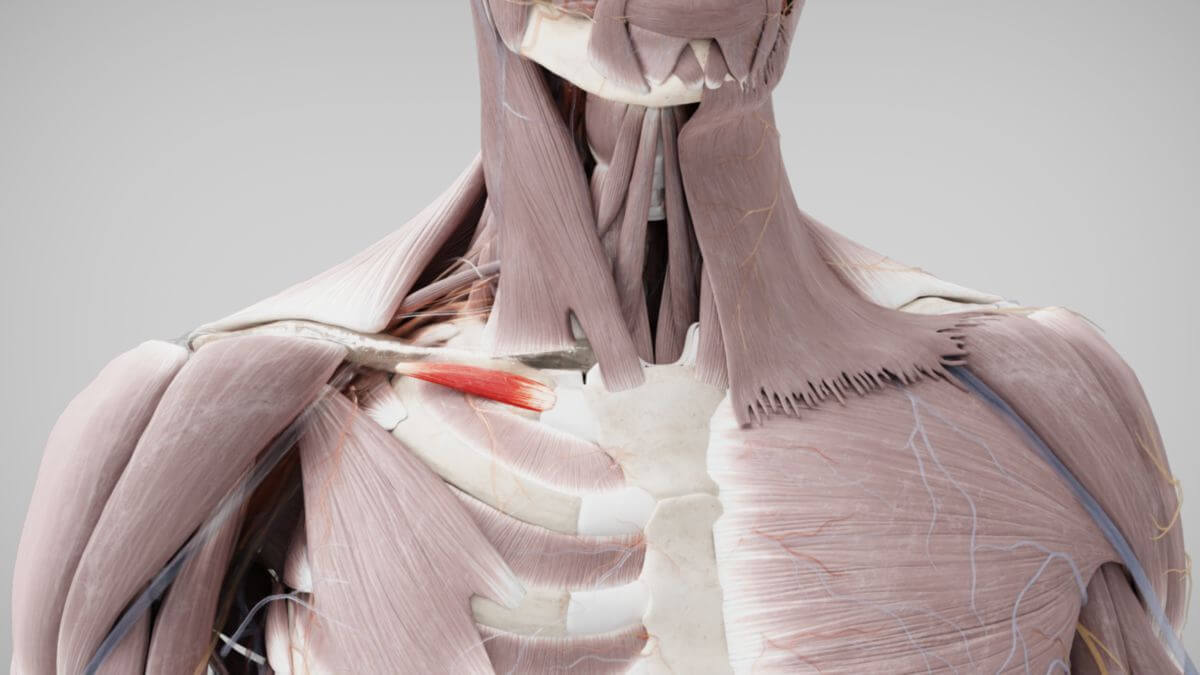
The '''subclavius muscle''' is a narrow | The '''subclavius muscle''' is a narrow, short [[Corpus:Muscle|muscle]] that lies between the first [[Ribose|rib]] and the [[Corpus:Clavicle|clavicle]]. <dcembed ratio="16x9"><dcEmbedUrl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/photos/43402-musculus-subclavius"></dcEmbedUrl> | ||
<dcEmbedUrl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/photos/43403-musculus-subclavius"></dcEmbedUrl></dcembed> | <dcEmbedUrl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/photos/43403-musculus-subclavius"></dcEmbedUrl></dcembed> | ||
== | ==Course== | ||
The | The subclavius muscle originates from the first rib and the first [[Corpus:Costal cartilage|costal cartilage]] via a strong, short [[Corpus:Tendon|tendon]]. Its muscle fibers then extend obliquely laterally and upward. The muscle inserts on the underside of the clavicle, specifically in the middle and lateral third, between the [[Corpus:Costoclavicular ligament|costoclavicular ligament]] and the [[Corpus:Conoid ligament|conoid ligament]]. | ||
<dcembed><dcembedurlskatchfab src="https://sketchfab.com/3d-models/6855d540ef4f4a2a8a82c28b013a108f" ui_controls="1"></dcembedurlskatchfab></dcembed> | <dcembed><dcembedurlskatchfab src="https://sketchfab.com/3d-models/6855d540ef4f4a2a8a82c28b013a108f" ui_controls="1"></dcembedurlskatchfab></dcembed> | ||
==Innervation== | ==Innervation== | ||
The subclavius muscle is innervated by the [[Corpus:Subclavian nerve|subclavian nerve]], which arises from the supraclavicular part of the [[Corpus:Brachial plexus|brachial plexus]], specifically from spinal segments C5 and C6. | |||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
The subclavius muscle | The subclavius muscle functions to pull the lateral end of the clavicle downward (caudally). Along with the [[Corpus:Pectoralis minor muscle|pectoralis minor muscle]], it helps keep the [[Corpus:Subclavian vein|subclavian vein]] open by stretching the [[Corpus:Clavipectoral fascia|clavipectoral fascia]]. Additionally, when the [[Corpus:Trapezius muscle|trapezius muscle]] lifts the [[Corpus:Thorax|thorax]], the subclavius muscle stabilizes the clavicle by anchoring it to the first rib. | ||
<dcembed ratio="16x9"><dcembedurl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/videos/3553-musculus-subclavius"></dcembedurl></dcembed> | <dcembed ratio="16x9"><dcembedurl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/videos/3553-musculus-subclavius"></dcembedurl></dcembed> | ||
==Clinic== | ==Clinic== | ||
Scar tissue shortening of the subclavius muscle can contribute to thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS), a condition that compresses the nerves and blood vessels passing through the thoracic outlet. | |||
[[Kategorie:Corpus]] | [[Kategorie:Corpus]] | ||
[[Kategorie:Head]] | [[Kategorie:Head]] | ||
[[Kategorie:Muscle]] | [[Kategorie:Muscle]] | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 11. September 2024, 15:42 Uhr
from Latin: clavus - nail
Definition
Course
The subclavius muscle originates from the first rib and the first costal cartilage via a strong, short tendon. Its muscle fibers then extend obliquely laterally and upward. The muscle inserts on the underside of the clavicle, specifically in the middle and lateral third, between the costoclavicular ligament and the conoid ligament.
Innervation
The subclavius muscle is innervated by the subclavian nerve, which arises from the supraclavicular part of the brachial plexus, specifically from spinal segments C5 and C6.
Function
The subclavius muscle functions to pull the lateral end of the clavicle downward (caudally). Along with the pectoralis minor muscle, it helps keep the subclavian vein open by stretching the clavipectoral fascia. Additionally, when the trapezius muscle lifts the thorax, the subclavius muscle stabilizes the clavicle by anchoring it to the first rib.
Clinic
Scar tissue shortening of the subclavius muscle can contribute to thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS), a condition that compresses the nerves and blood vessels passing through the thoracic outlet.