Corpus: Spinalis muscles: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(Englische Seite angelegt) |
KKeine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
||
| (5 dazwischenliegende Versionen von 3 Benutzern werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
==Definition== | ==Definition== | ||
The ''' | The '''spinalis muscles''' are part of the interspinal system within the [[Corpus:Autochthonous back muscles|autochthonous back muscles]].<dcembed ratio="16x9"><dcEmbedUrl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/photos/42966-musculi-spinales"></dcEmbedUrl> | ||
<dcEmbedUrl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/photos/42967-musculi-spinales"></dcEmbedUrl> | <dcEmbedUrl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/photos/42967-musculi-spinales"></dcEmbedUrl> | ||
<dcEmbedUrl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/photos/42965-musculi-spinales"></dcEmbedUrl></dcembed> | <dcEmbedUrl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/photos/42965-musculi-spinales"></dcEmbedUrl></dcembed> | ||
| Zeile 10: | Zeile 6: | ||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
The spinal muscles can be regionally divided into three parts: | The spinal muscles can be regionally divided into three parts: | ||
* Spinalis thoracis muscle | |||
* Spinalis cervicis muscle | |||
* Spinalis capitis muscle (often absent in most people) | |||
==Course== | ==Course== | ||
===Origin=== | ===Origin=== | ||
The spinalis thoracis muscle originates | The spinalis thoracis muscle originates from the [[Corpus:Spinous processes|spinous processes]] of the lower [[Corpus:Thoracic vertebra|thoracic vertebrae]] (T10, T11, T12) and the 1st and 2nd [[Corpus:Lumbar vertebra|lumbar vertebrae]] (L1, L2). The spinalis cervicis muscle originates from the spinous processes of the 4th to 7th [[Corpus:Cervical vertebra|cervical vertebrae]] (C4-C7). The spinalis capitis muscle, if present, originates from the spinous processes of the lower [[Corpus:Cervical vertebra|cervical]] and upper thoracic vertebrae. | ||
The | |||
The spinalis | ===Attachment=== | ||
The spinalis thoracis muscle attaches to the spinous processes of the upper thoracic vertebrae. The spinalis cervicis muscle attaches to the spinous processes of the 2nd and 3rd cervical vertebrae (C2, C3). The spinalis capitis muscle attaches between the [[Corpus:Superior nuchal line|superior]] and [[Corpus:Inferior nuchal line|inferior nuchal lines]] of the [[Corpus:Occipital bone|occipital bone]], along with the [[Corpus:Semispinalis muscle|semispinalis capitis muscle]]. | |||
<dcembed ratio="16x9"><dcEmbedUrl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/videos/3591-musculi-spinales"></dcEmbedUrl></dcembed> | |||
<dcembed>< | |||
==Innervation== | ==Innervation== | ||
The spinal muscles are innervated by the medial branches of the posterior | The spinal muscles are innervated by the medial branches of the posterior branch of the respective segmental [[Corpus:Spinal nerve|spinal nerves]]. | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
The spinal muscles in the cervical and thoracic | The spinal muscles in the cervical and thoracic regions extend the [[Corpus:Spinal column|spinal column]]. The spinalis capitis muscle, when present, functions in unilateral rotation of the head to the opposite side and bilateral dorsiflexion in the [[Corpus:Atlantooccipital joint|atlantooccipital joint]] and the [[Corpus:Cervical spine|cervical spine]]. | ||
The | |||
[[Kategorie:Corpus]] | [[Kategorie:Corpus]] | ||
[[Kategorie:Head]] | [[Kategorie:Head]] | ||
[[Kategorie:Muscle]] | [[Kategorie:Muscle]] | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 21. August 2024, 12:11 Uhr
Definition
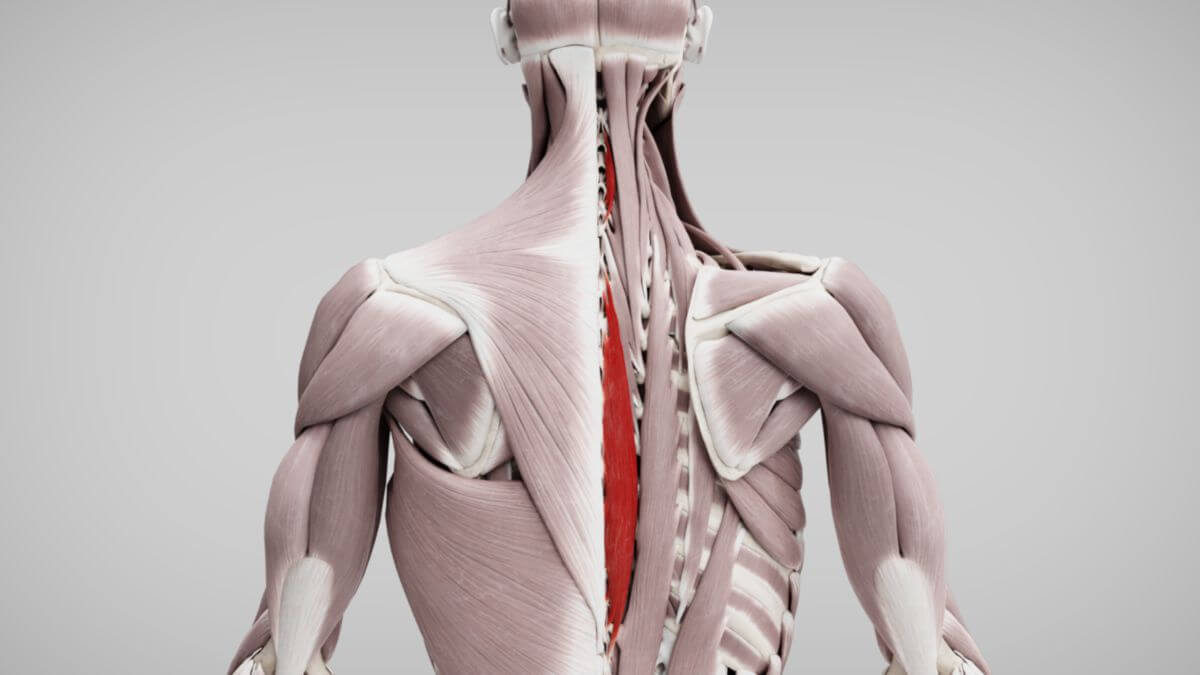
The spinalis muscles are part of the interspinal system within the autochthonous back muscles.
Classification
The spinal muscles can be regionally divided into three parts:
- Spinalis thoracis muscle
- Spinalis cervicis muscle
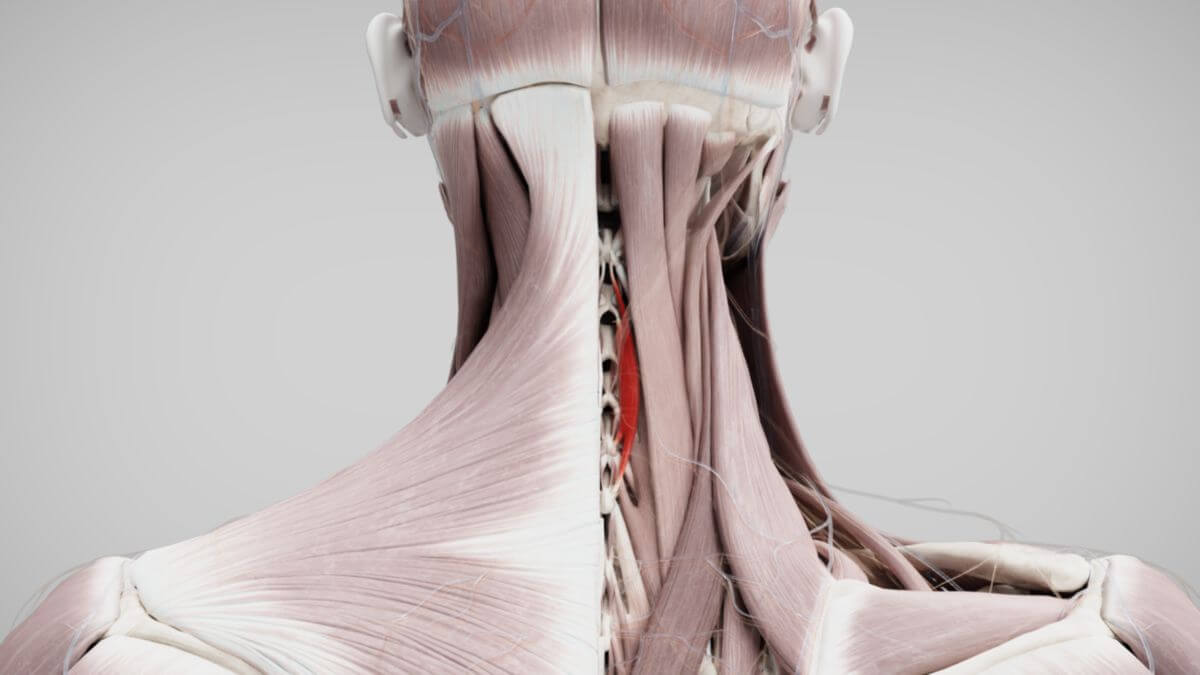
- Spinalis capitis muscle (often absent in most people)
Course
Origin
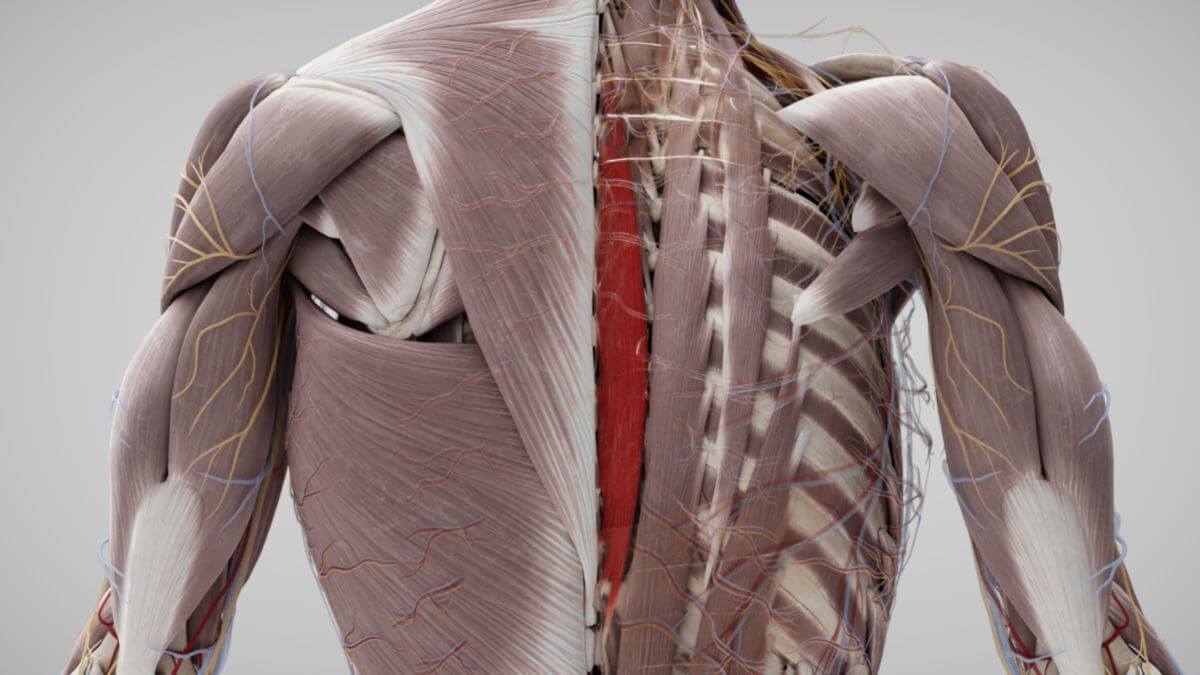
The spinalis thoracis muscle originates from the spinous processes of the lower thoracic vertebrae (T10, T11, T12) and the 1st and 2nd lumbar vertebrae (L1, L2). The spinalis cervicis muscle originates from the spinous processes of the 4th to 7th cervical vertebrae (C4-C7). The spinalis capitis muscle, if present, originates from the spinous processes of the lower cervical and upper thoracic vertebrae.
Attachment
The spinalis thoracis muscle attaches to the spinous processes of the upper thoracic vertebrae. The spinalis cervicis muscle attaches to the spinous processes of the 2nd and 3rd cervical vertebrae (C2, C3). The spinalis capitis muscle attaches between the superior and inferior nuchal lines of the occipital bone, along with the semispinalis capitis muscle.
Innervation
The spinal muscles are innervated by the medial branches of the posterior branch of the respective segmental spinal nerves.
Function
The spinal muscles in the cervical and thoracic regions extend the spinal column. The spinalis capitis muscle, when present, functions in unilateral rotation of the head to the opposite side and bilateral dorsiflexion in the atlantooccipital joint and the cervical spine.