Corpus: Semispinalis muscle
1. Definition
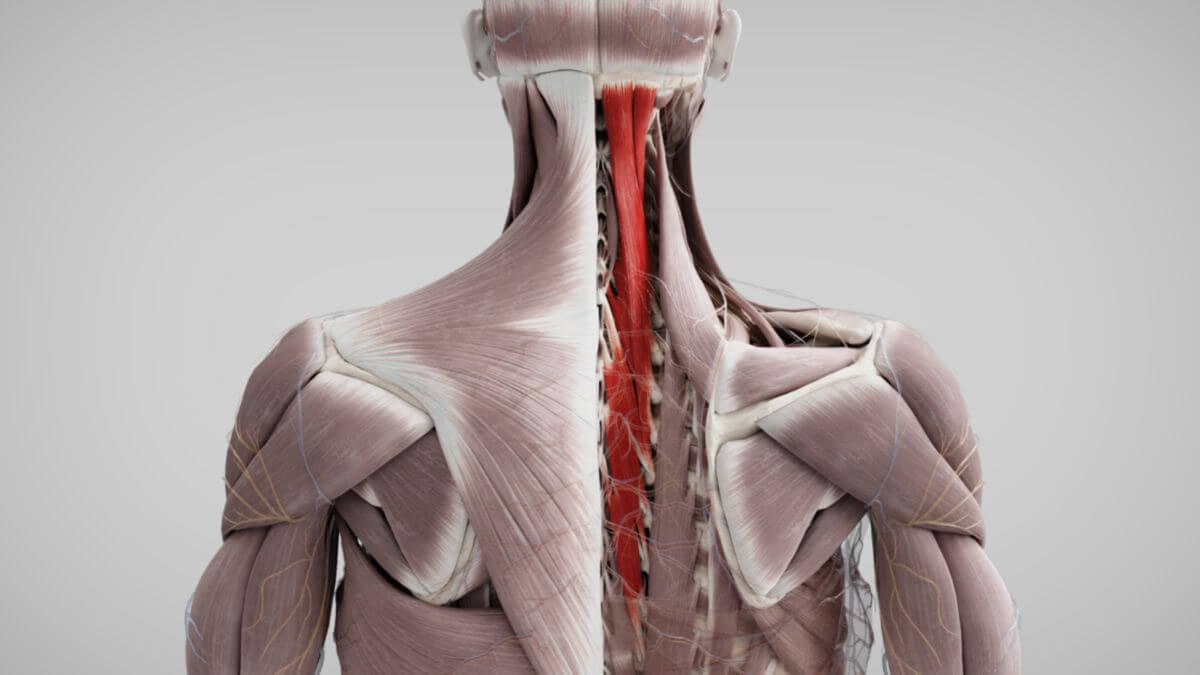
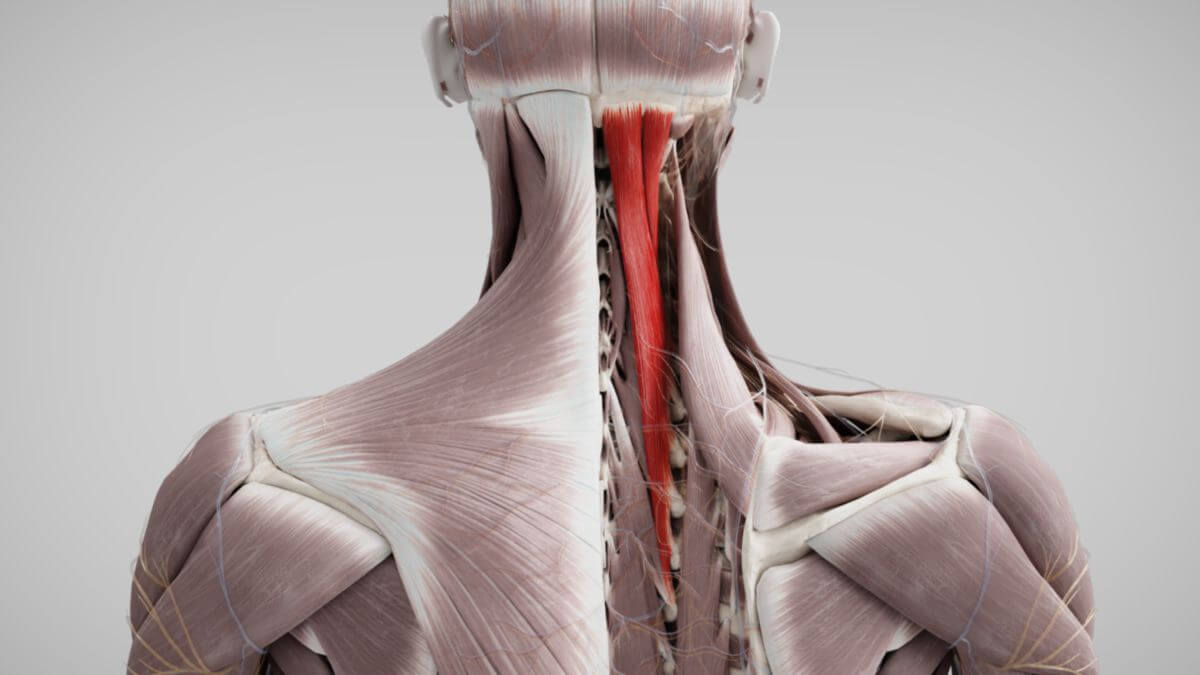
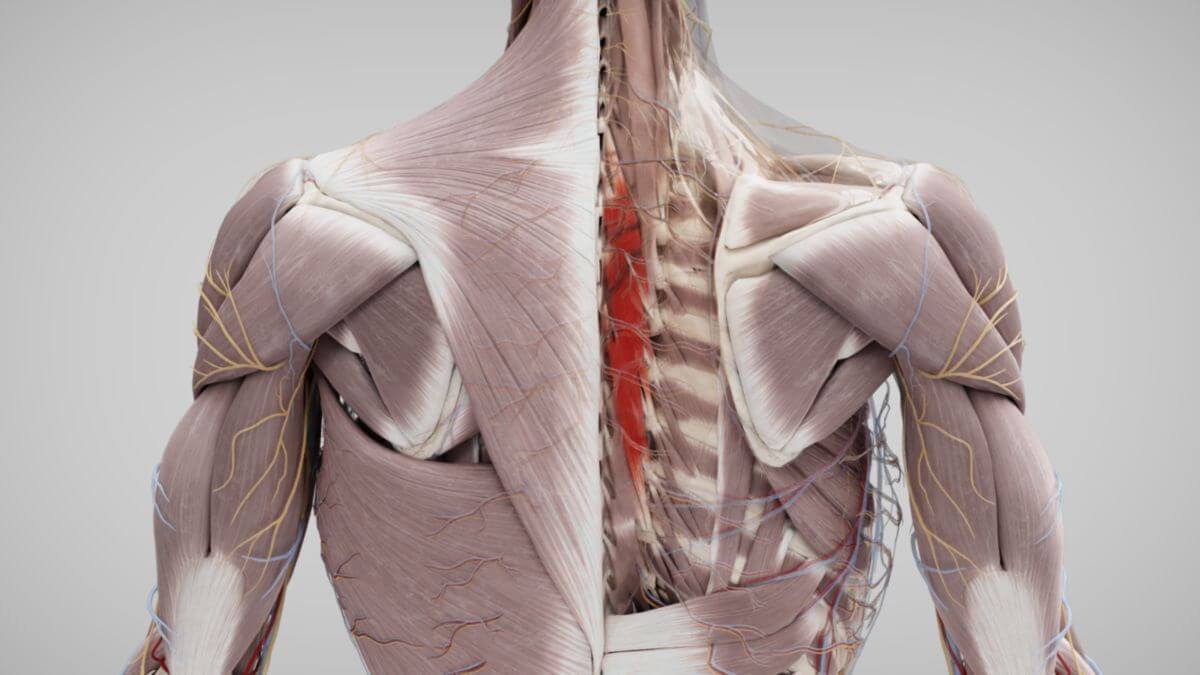
The semispinalis muscles are skeletal muscles that form part of the back musculature. They belong to the medial tract of the erector spinae muscle group.
2. Anatomy
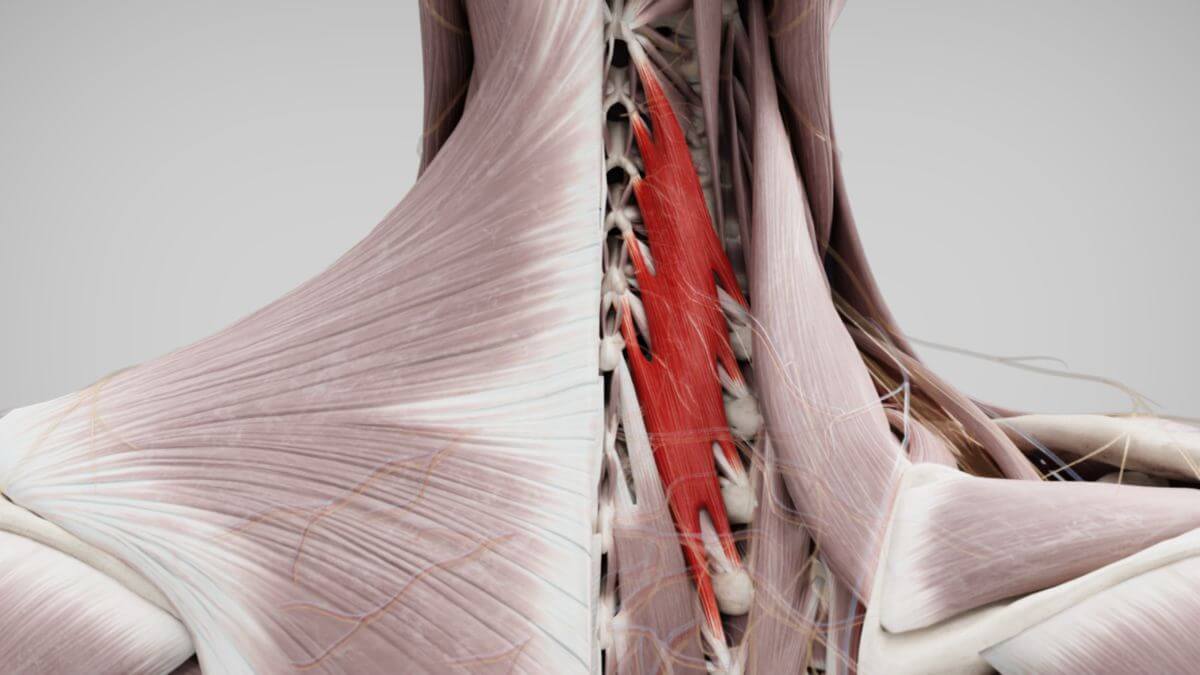
The semispinalis muscles are located in the regions of the head, cervical, and thoracic spine. These muscles originate from the transverse processes (or homologous areas) and typically attach 6 to 7 vertebral levels higher to the spinous processes or the occipital bone.
To aid in orientation, the semispinalis muscles are divided into three groups:
- Musculus semispinalis capitis
- Musculus semispinalis cervicis
- Musculus semispinalis thoracis
2.1. Musculus semispinalis capitis
The muscle fibers of the semispinalis capitis muscle originate from the articular processes of thoracic vertebrae T6 to cervical vertebrae C3. They attach to the medial area of the occipital bone, specifically between the superior and inferior nuchal lines.
2.2. Musculus semispinalis cervicis
The semispinalis cervicis muscle originates from the transverse processes of thoracic vertebrae T7 to T2, with insertions extending from cervical vertebrae C6 to C2.
2.3. Musculus semispinalis thoracis
The semispinalis thoracis muscle originates from the transverse processes of thoracic vertebrae T12 to T7, with corresponding insertions extending from the spinous processes of thoracic vertebrae T4 to cervical vertebrae C6.
3. Innervation
The semispinalis muscles are innervated by the medial branches of the posterior rami from the respective segmental spinal nerves. The semispinalis capitis muscle may also receive innervation from the lateral branches of the posterior rami.
4. Function
The semispinalis capitis muscle, when contracted on one side, rotates the head to the opposite side. When both sides contract, the head is dorsiflexed (extended). The semispinalis cervicis and thoracis muscles, when contracted unilaterally, rotate the respective spinal region to the opposite side, resulting in lateral flexion to the same side. Bilateral contraction of these muscles contributes to the extension of the spine.