Corpus: Rib
1. Definition
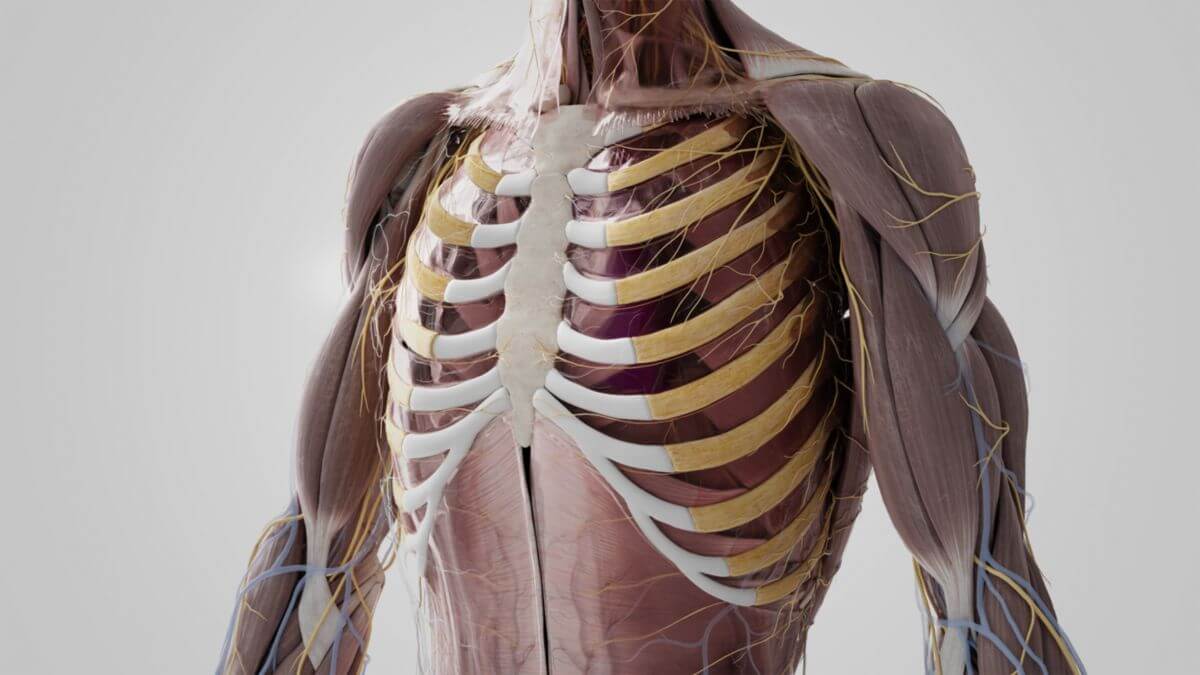
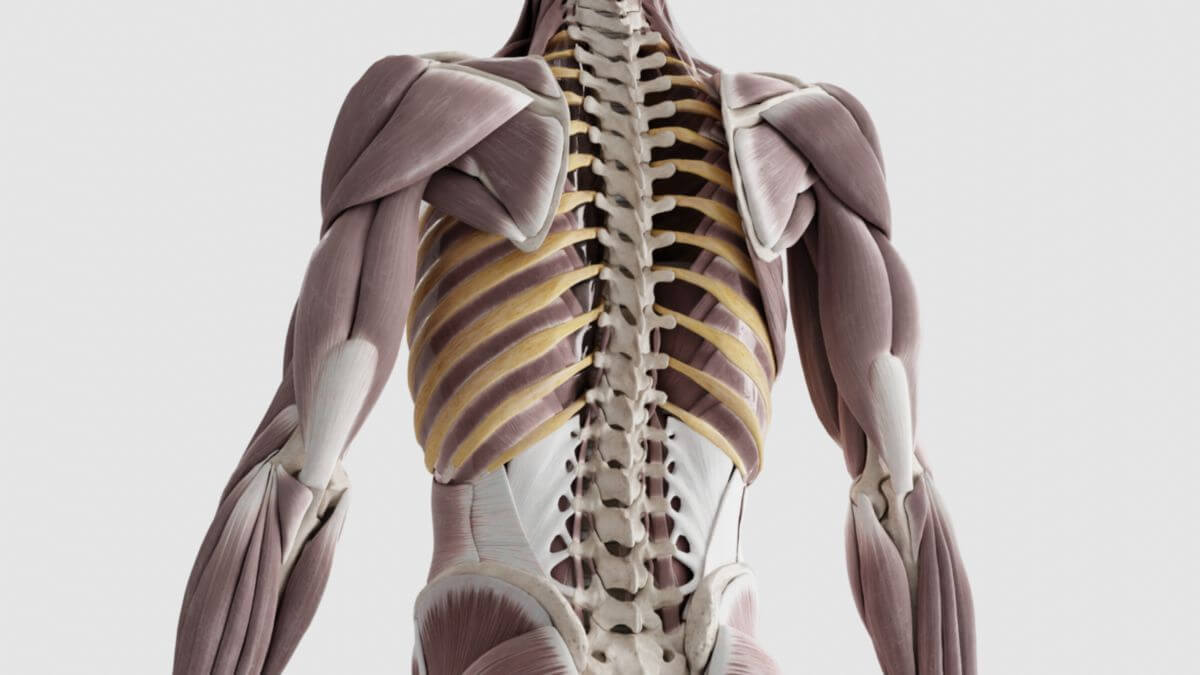
The term ribs refers to the paired, curved, rod-shaped bones that originate on the dorsal side of the thoracic spine. Together with the thoracic spine and the sternum, they form the bony rib cage, or thorax.
2. Anatomy
The number of ribs corresponds to the number of thoracic vertebrae. Humans have a total of 12 pairs of ribs. Each rib consists of a bony part and an adjoining section of cartilage, known as the costal cartilage. The space between two consecutive ribs is known as the intercostal space, which is partly filled by the intercostal muscles. The articular connections between the cartilages of the 6th to 10th ribs are known as the interchondral joints.
2.1. Classification
The first rib is positioned between the last cervical vertebra (C7) and the first thoracic vertebra (Th1). In humans, the upper 7 ribs are directly connected to the sternum via the costal cartilage, and are referred to as "true" or "sternal" ribs. Ribs 8 to 12 are attached to the cartilaginous costal arch and are called "false" or "asternal" ribs. The last two ribs (11th and 12th) are rudimentary and end freely in the abdominal wall, known as "floating ribs".
| Rib | Latin name | English name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 to 7 | Costae verae | True ribs |
| 8 to 12 | Costae spuriae | False ribs |
| 8, 9, 10 | Costae affixae | Fixed ribs |
| 11, 12 | Costae fluctuantes | Floating ribs |
2.2. Common characteristics
Ribs can be divided into the following sections:
- Rib head
- Rib neck
- Rib body
The rib head is connected to the spinal column, articulating with two consecutive vertebrae. The articular surface of the rib head is divided into two parts. The rib tubercle, located at the rib neck, articulates with the transverse process of the corresponding thoracic vertebra via a small articular surface. Near the rib neck is the rib angle. The rib body has a convex outer surface and a concave inner surface. The intercostal nerves and associated blood vessels run along the lower edge in a bony groove, the sulcus costae.
2.3. Peculiarities
| Name | Latin | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| 1st rib | Costa I (prima) | True rib, shortest and most curved, with sulci for neighboring structures; insertion of scalenus anterior and scalenus medius muscles, origin of serratus anterior muscle (superior part) |
| 2nd rib | Costa II (seconda) | True rib, strongly curved, longer than the 1st rib; insertion of posterior and medial scalene muscles, origin of serratus anterior muscle (superior and intermedial parts) |
| 3rd rib | Costa III (tertia) | True rib, origin of serratus anterior muscle (intermedial part), possibly also insertion of the scalenus posterior muscle |
| 4th rib | Costa IV (quarta) | True rib, origin of serratus anterior muscle (inferior part) |
| 5th rib | Costa V (quinta) | True rib, origin of serratus anterior muscle (inferior part) |
| 6th rib | Costa VI (sexta) | True rib, origin of serratus anterior muscle (inferior part) |
| 7th rib | Costa VII (septima) | True rib, origin of serratus anterior muscle (inferior part) |
| 8th rib | Costa VIII (octava) | False rib, origin of serratus anterior muscle (inferior part) |
| 9th rib | Costa IX (nona) | False rib, origin of serratus anterior muscle (inferior part), lies anteriorly on the Addison plane |
| 10th rib | Costa X (decima) | False rib |
| 11th rib | Costa XI (undecima) | False rib, ends free |
| 12th rib | Costa XII (duodecima) | False rib, ends free |
2.4. Variants
Anatomical malformations or variations of the ribs can occur, including:
- Accessory Ribs:
- Cervical ribs
- Lumbar ribs
- Minus Variants (Complete or partial absence of ribs):
- Srb anomaly (underdevelopment of the 1st rib)
- missing lower ribs
- Forked Rib
- Bony Congenital Rib Bridges: Usually between upper ribs, sometimes due to trauma
- Rib Fusions: Often associated with conditions like Klippel-Feil syndrome or scapular protrusion
- Intrathoracic Ribs: Rare, inward-pointing small ribs.
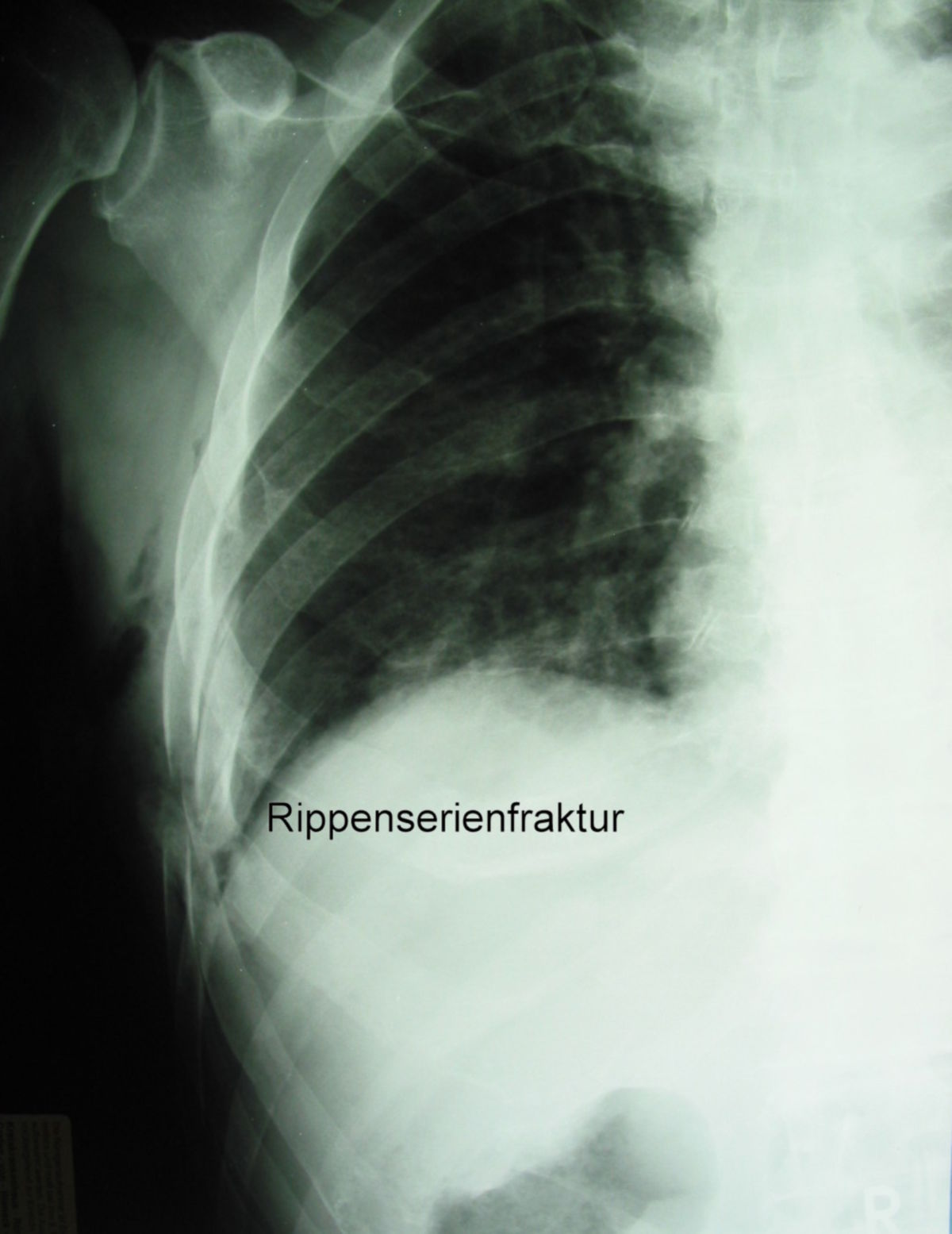
3. Clinical
Due to their shape and exposed position, ribs are susceptible to injury in accidents. Rib contusions and rib fractures are relatively common conditions encountered in trauma surgery.