Corpus: Palatine bone
1. Definition
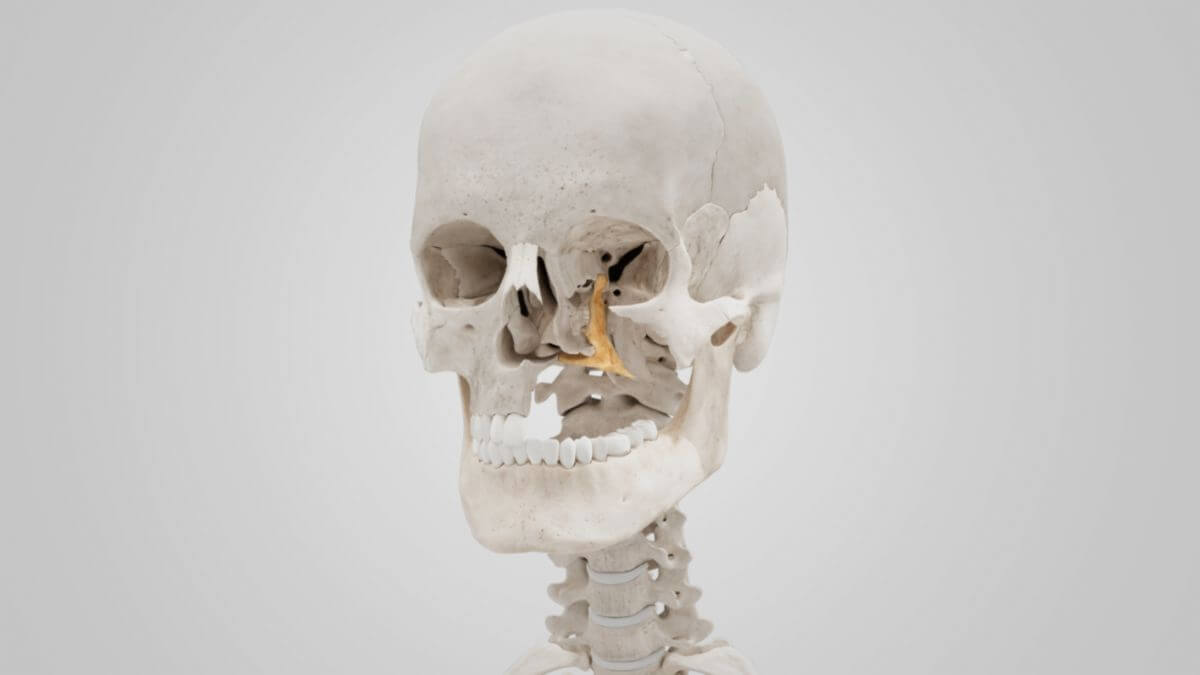
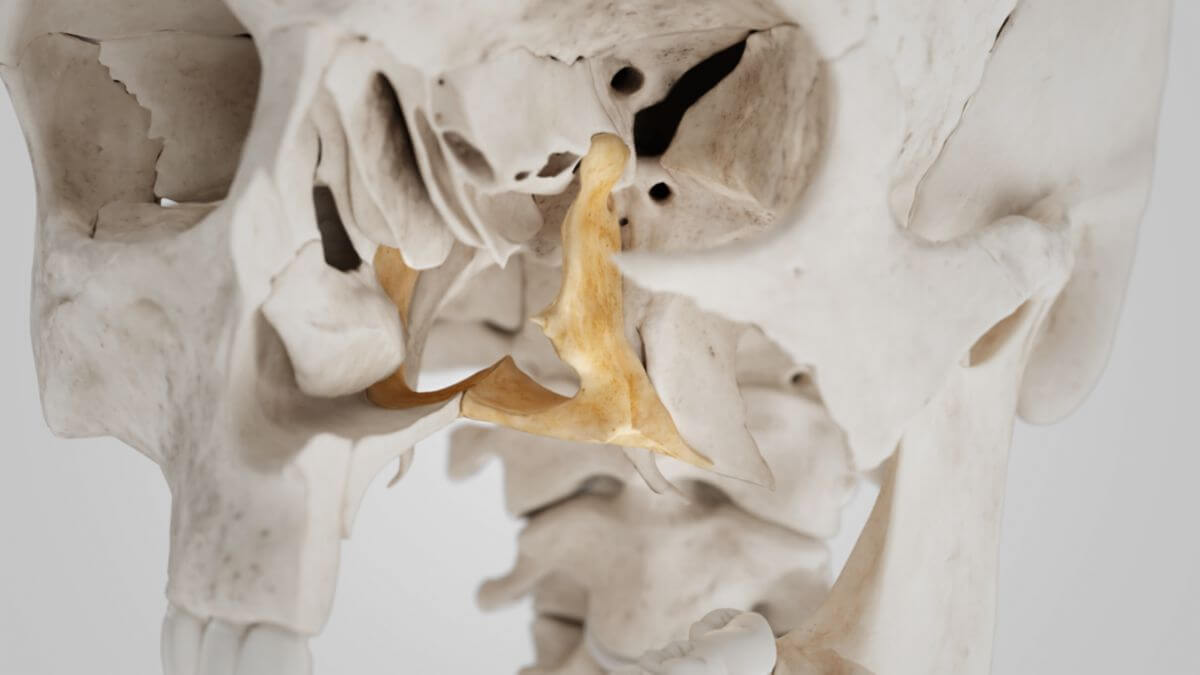
The palatine bone is a bone of the facial skull (splanchnocranium). Along with the maxilla, it helps to form the boundaries of the oral and nasal cavities and supports the posterior part of the hard palate.
2. Anatomy
The palatine bone is divided into two main parts: the horizontal plate and the perpendicular plate. The horizontal plate comprises a portion of the hard palate and is connected to the vomer. Its posterior edge delimits the opening of the choanae (posterior nasal apertures). Together with the maxilla and the sphenoid bone, the perpendicular plate forms the pterygopalatine fossa.
The horizontal plate primarily contributes to the structure of the hard palate, providing support and separating the oral and nasal cavities. The perpendicular plate extends vertically, playing a role in comprising the lateral walls of the nasal cavity and the floor of the orbit.