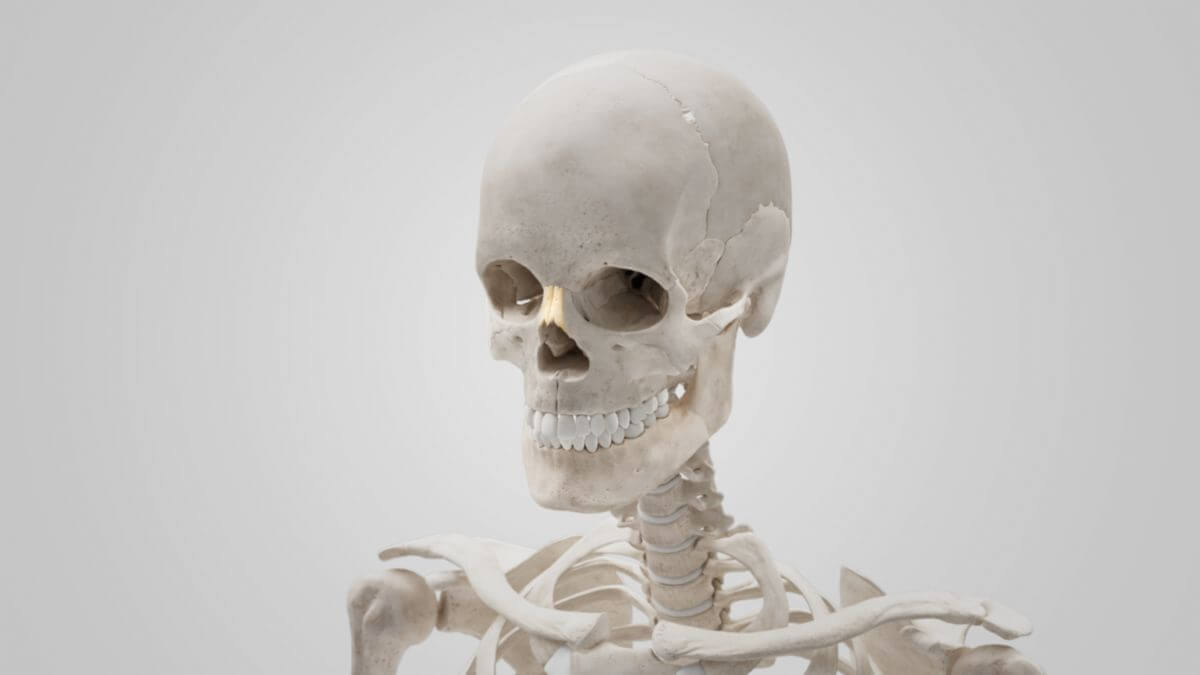
Corpus: Nasal bone
1. Definition
2. Anatomy
2.1. Surfaces
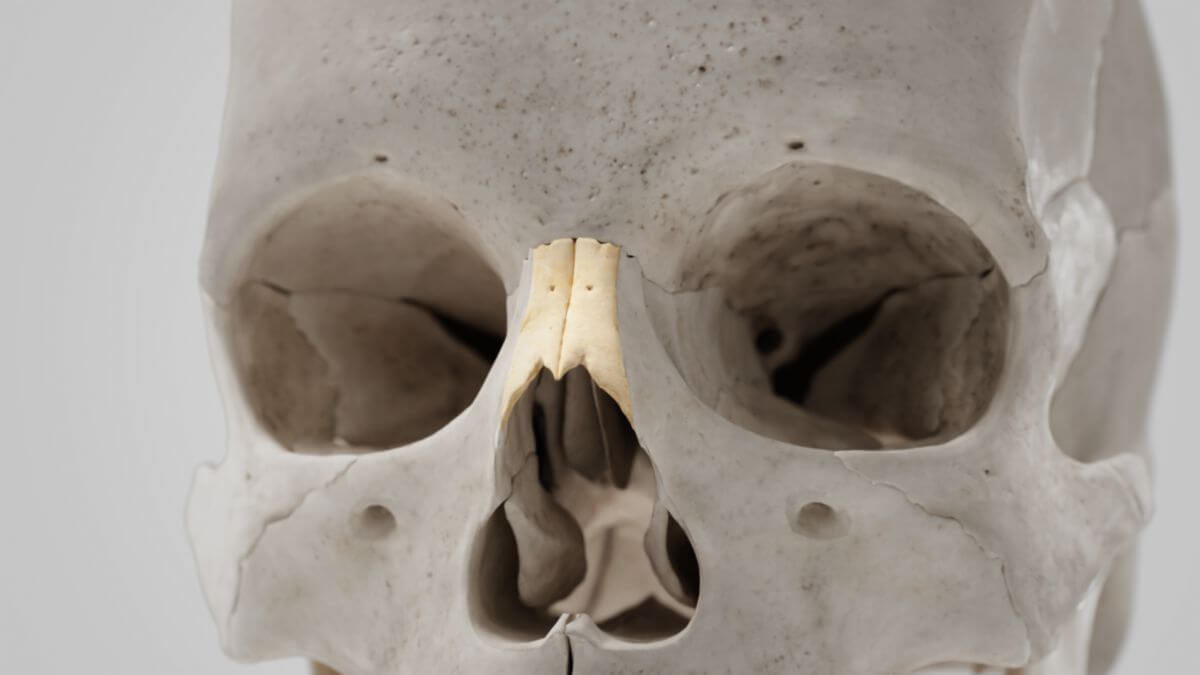
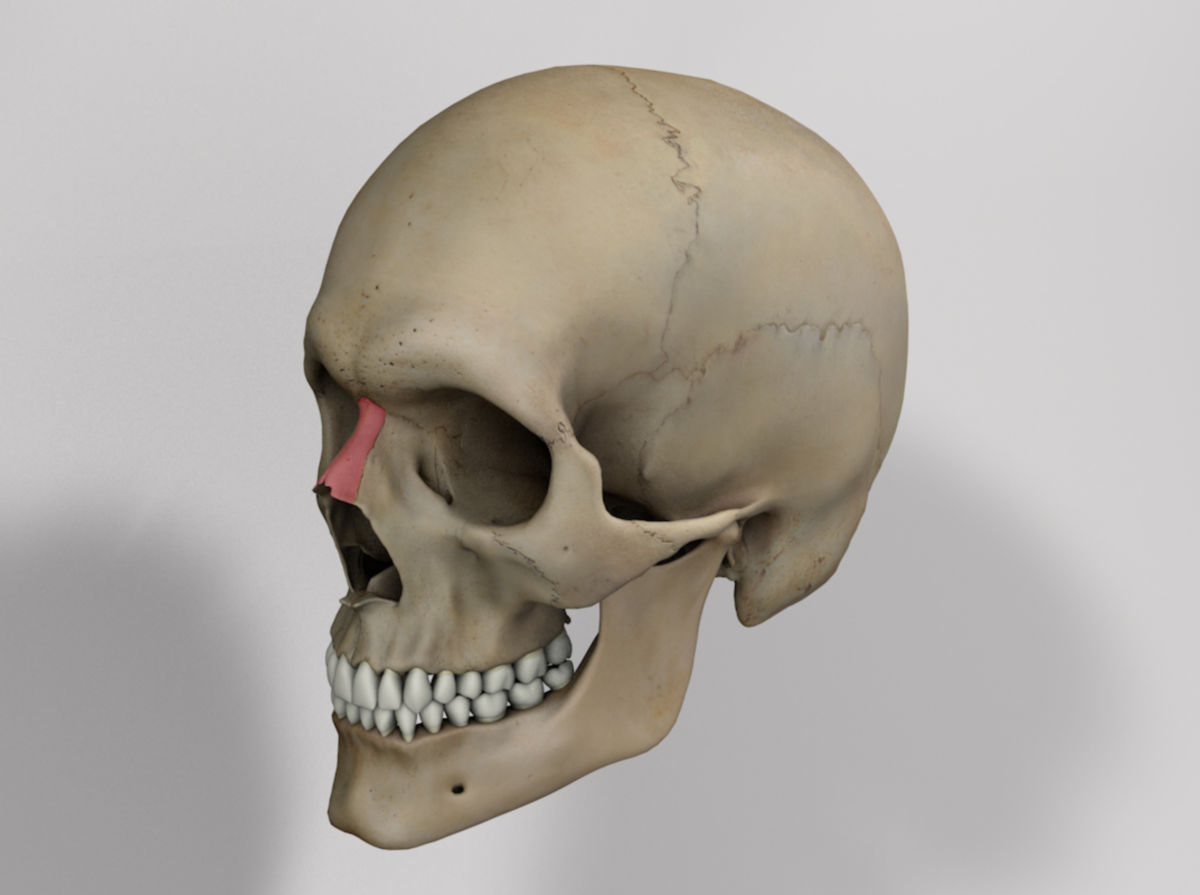
The outer surface of the nasal bone is concave in the longitudinal direction and convex in the transverse direction. A small perforation for a vein is visible approximately in the center of the bone. The inner surface facing the nasal cavity shows a longitudinal groove for the nasociliary nerve. The suture between the right and left nasal bones is called the internasal suture. Together with the glabella of the frontal bone, the two nasal bones form the nasofrontal suture, with the most anterior point referred to as the "nasion." The nasal bones are not involved in the formation of the orbit.
2.2. Margins
The nasal bone is associated with the following structures:
| Margin | Neighboring structure | Sutur |
|---|---|---|
| Superior margin | Frontal bone | Nasofrontal suture |
| Medial margin | Nasal bone of the opposite side | Internasal suture |
| Lateral margin | Frontal process of the maxilla | Nasomaxillary suture |
The inferior margin of the nasal bone merges into the lateral nasal cartilage. Dorsally, the nasal bone connects to the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone.
3. Embryology
Ossification of the nasal bone starts in the 8th embryonic week and is completed before birth.
4. Clinic
Due to its exposed position, the nasal bone is susceptible to fractures from violent impacts to the face.