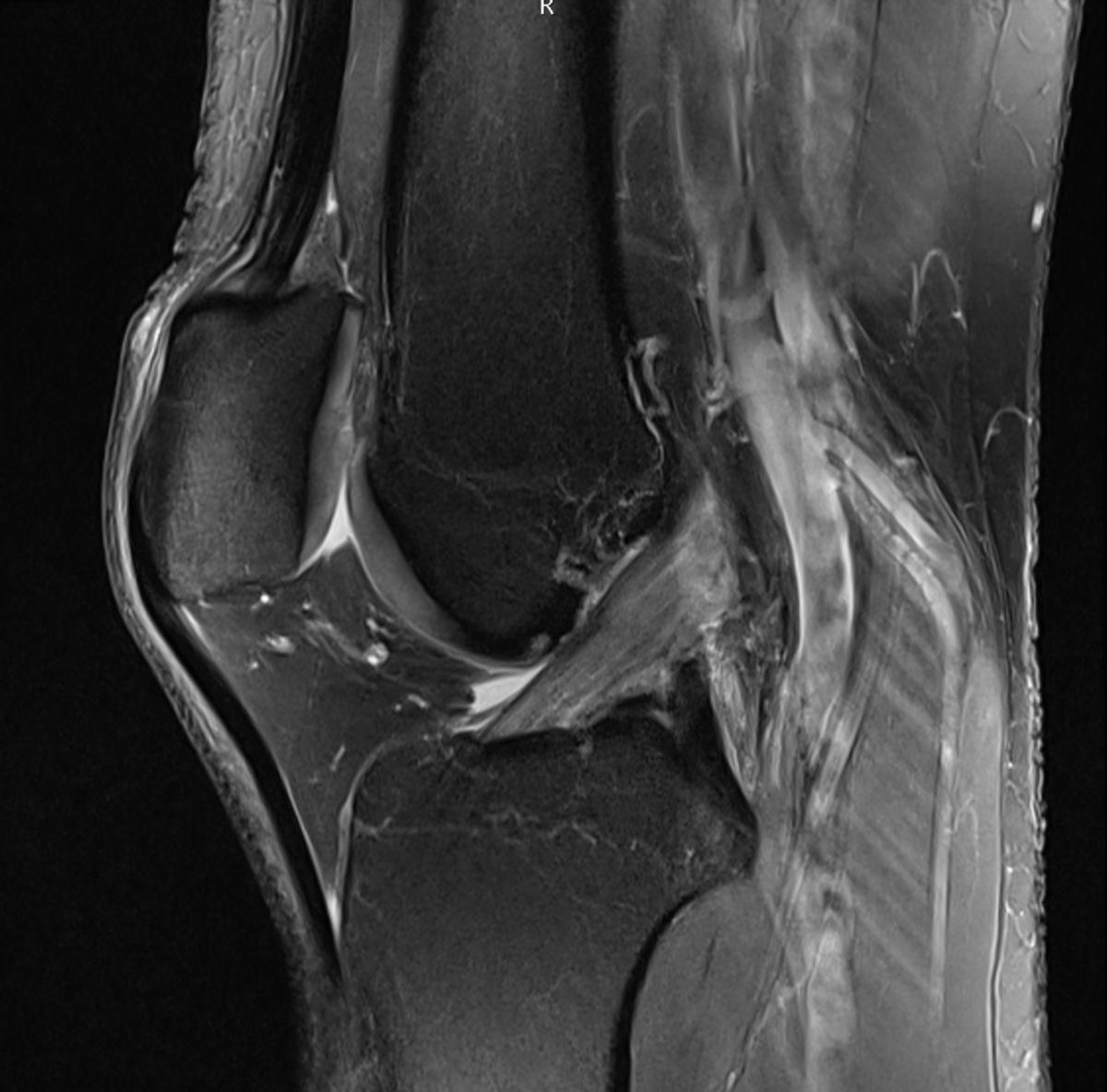
Corpus: Anterior cruciate ligament
1. Definition
The anterior cruciate ligament, or ACL for short, is a component of the ligamentous structures of the knee joint.
2. Anatomy
The anterior cruciate ligament connects the femur to the tibia. It extends from the lateral condyle of the femur, specifically from the lateral wall of the intercondylar fossa, to the anterior intercondylar area in front of the intercondylar eminence of the tibia.
The anterior cruciate ligament runs from posterior, superior, and lateral (back-top-outside) to anterior, inferior, and medial (front-bottom-inside), in the opposite direction to the posterior cruciate ligament.
2.1. Functional categorization
In the literature, the ACL is often categorized into two main bundles:
- Anteromedial bundle (AM bundle): originates from the femur near the intercondylar line and inserts in the anterior region of the tibial plateau.
- Posterolateral bundle (PL bundle): originates along the cartilage-bone boundary of the femoral condyles and inserts in the posterior region near the medial meniscus.
These bundles lie one behind the other in the intercondylar fossa, giving the ACL an oval cross-section.
2.2. Arterial supply
The anterior cruciate ligament receives its arterial supply proximally from the end branches of the middle genicular artery and distally from the end branches of the medial inferior genicular artery and the lateral inferior genicular artery. The distribution of blood vessels within the ligament is uneven, with the center and the apophyseal insertion zones being largely avascular.
3. Function
The anterior cruciate ligament is considered by some authors to be the most crucial and heavily loaded ligament of the knee joint. Along with the posterior cruciate ligament and the collateral ligaments, it stabilizes the knee joint. The AM bundle is particularly tense during flexion, while the PL bundle is tense during extension and rotation.
The anterior cruciate ligament primarily restricts forward displacement of the tibia, especially in a 20° to 30° flexed position, and prevents excessive internal rotation in combination with the posterior cruciate ligament. It also supports the collateral ligaments of the knee joint to a lesser extent.
The anterior cruciate ligament plays a significant role in proprioception due to its numerous mechanoreceptors.
4. Clinic
The ACL is the most frequently injured ligament in the knee, particularly in sports. A rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament, often due to overloading, can be diagnosed using the drawer test, where the tibia can be pulled forward relative to the femur ("anterior drawer"). Other clinical tests for detecting an ACL rupture include the Lachman test and the pivot shift test. Confirmation of the diagnosis can be confirmed with an MRI of the knee joint.