Corpus: Bundle of His
Achtung: Du siehst nicht die aktuelle, sondern eine ältere Version dieser Seite.
This text has been translated by an AI and may sound raw. It will be reviewed shortly. Thank you for your patience!
This text has been translated by an AI and may sound raw. It will be reviewed shortly. Thank you for your patience!
after the German internist Wilhelm His (1863-1934)
1. Definition
The His bundle is a crucial component of the cardiac conduction system.
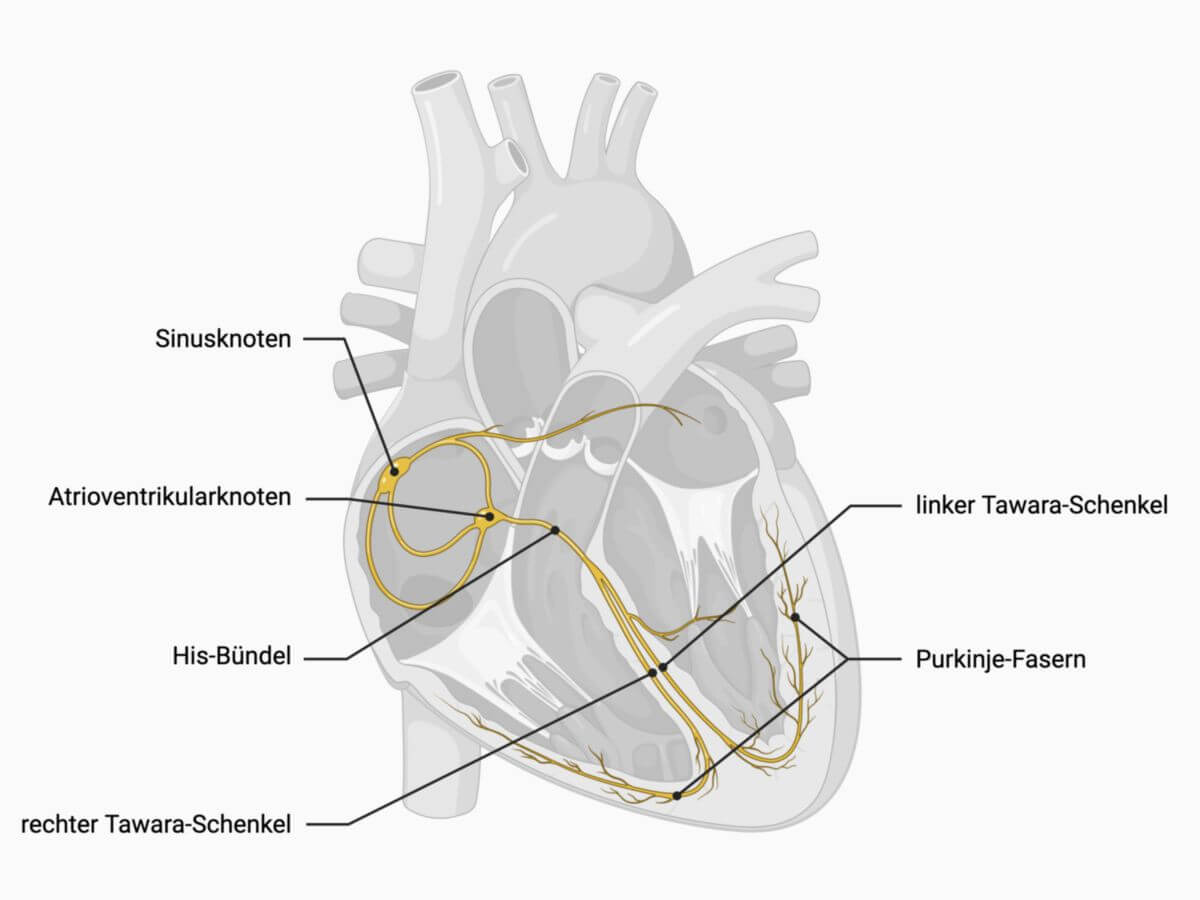
2. Anatomy
The His bundle is about 4 mm thick and 20 mm long. It begins at the atrioventricular node, running subendocardially in the atrium, perforating the right fibrous trigone of the cardiac skeleton, and then dividing into the Tawara branches within the membranous part of the ventricular septum. Similar to the ventricular legs, the His bundle is insulated from the surrounding working myocardium by connective tissue sheaths.
3. Physiology
Normal cardiac excitation starts at the sinus node, the heart’s primary pacemaker, which generates 60 to 80 impulses per minute. These impulses travel through the right atrium to the AV node. If the sinus node fails or if there's an AV block (impairment in transmission), the AV node can act as a secondary pacemaker, producing 40 to 50 impulses per minute.
The His bundle transmits the excitation from the AV node and splits into the Tawara branches, which extend into the ventricles as Purkinje fibres, ensuring coordinated and complete ventricular contraction.
4. Pathophysiology
If both the sinus and atrioventricular nodes fail, the His bundle can generate its own rhythm, called a ventricular escape beat, which has a very slow rate of 20 to 30 beats per minute. This rate is insufficient to maintain adequate blood circulation, and immediate pacemaker implantation is typically necessary to ensure a proper blood supply.
Disorders associated with the His bundle include bundle branch block as well as the rarer condition of congenital His bundle tachycardia or junctional ectopic tachycardia, which can occur in newborns and infants up to 6 months of age.
These conduction abnormalities can be detected on a surface ECG (electrocardiogram) and further detailed through a His bundle ECG.