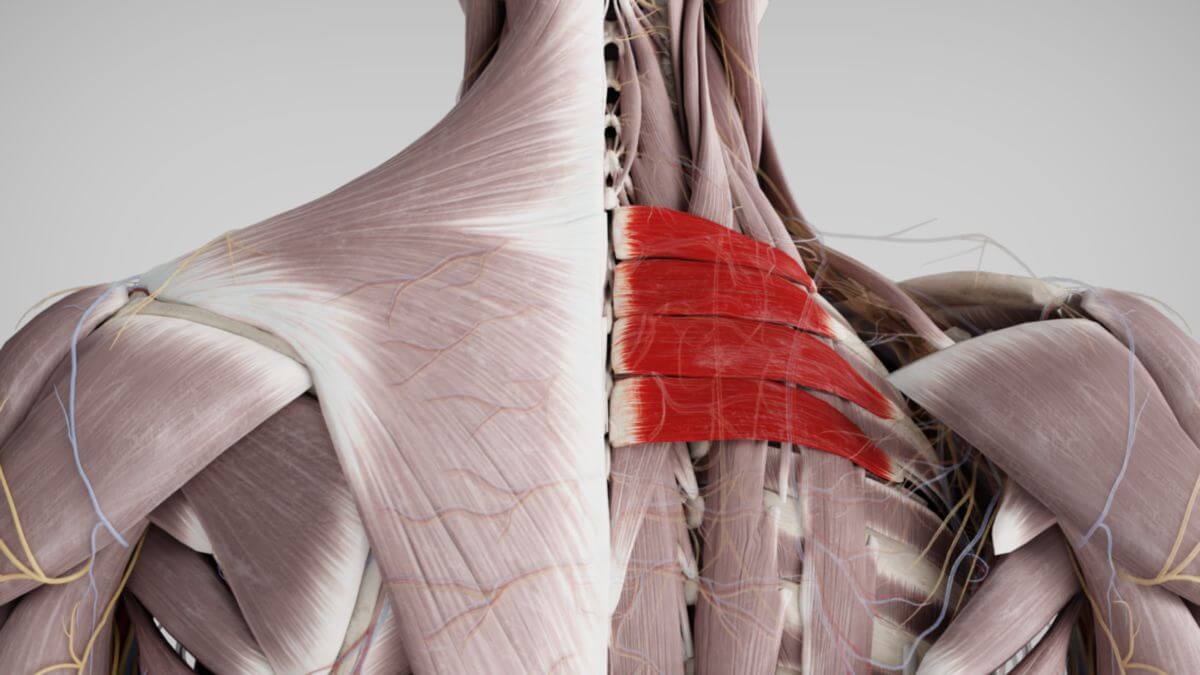
Corpus: Serratus posterior superior muscle
Achtung: Du siehst nicht die aktuelle, sondern eine ältere Version dieser Seite.
This text has been translated by an AI and may sound raw. It will be reviewed shortly. Thank you for your patience!
This text has been translated by an AI and may sound raw. It will be reviewed shortly. Thank you for your patience!
1. Definition
The posterior superior serratus muscle is part of the deep layer of the secondary migratory back muscles. These muscles initially develop from the limb buds and later migrate into the back, and they are typically innervated by the anterior rami of the spinal nerves.
2. Course
2.1. Origin
The posterior superior serratus muscle originates with a thin aponeurosis from the spinous processes of the two lowest cervical vertebrae (C6 and C7) and the two uppermost thoracic vertebrae (T1 and T2).
2.2. Appendix
The 3 to 4 descending muscle prongs of the posterior superior serratus muscle insert on the 2nd or 3rd to 5th ribs, lateral to the angulus costae.
3. Innervation
The posterior superior serratus muscle is innervated by the anterior branches (rami anteriores) of the spinal nerves, specifically from segments Th2 to Th5.
4. Function
The posterior superior serratus muscle functions to lift the ribs, thereby supporting inspiration. This function is facilitated by the muscle's favorable leverage, due to its course relative to the axis of the costovertebral joints, allowing it to effectively assist in the process of inhalation.