Corpus: Stylohyoid muscle: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
K (Schützte „Corpus:Stylohyoid muscle“ ([Bearbeiten=Nur Administratoren erlauben] (unbeschränkt) [Verschieben=Nur Administratoren erlauben] (unbeschränkt))) |
K (englischen Artikel überarbeitet) |
||
| Zeile 2: | Zeile 2: | ||
==Definition== | ==Definition== | ||
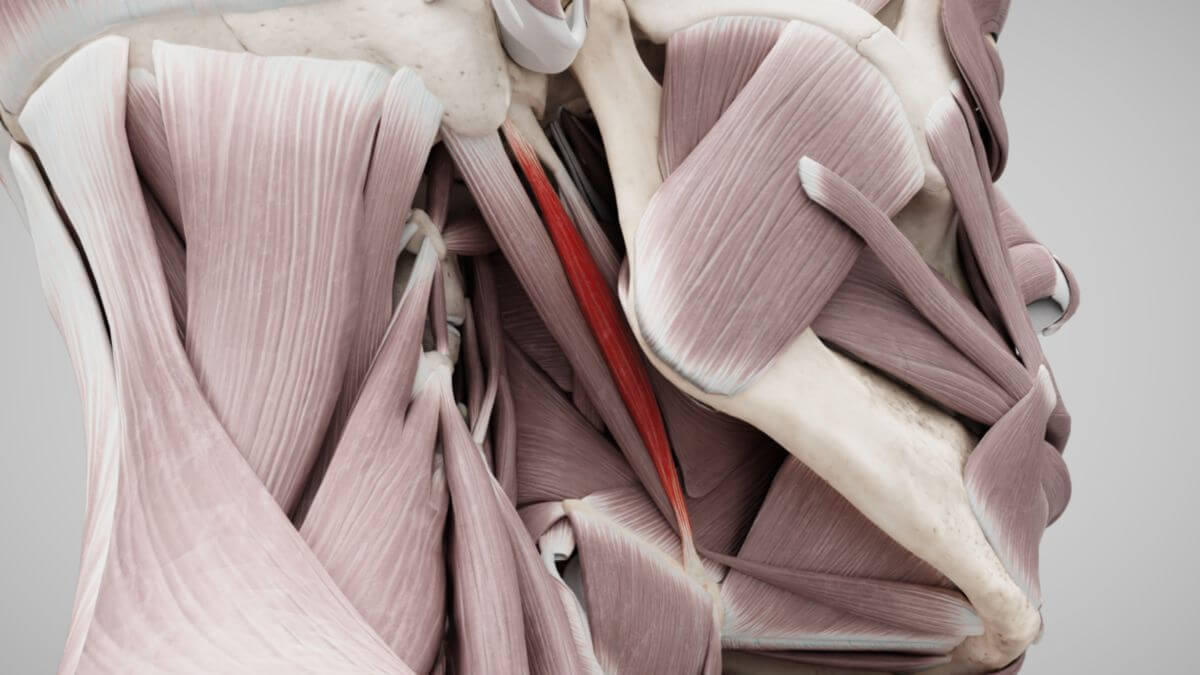
The '''stylohyoid muscle''' is a slender skeletal muscle in the transition area between the head and neck, | The '''stylohyoid muscle''' is a slender [[Corpus:Muscle|skeletal muscle]] located in the transition area between the [[Corpus:Head|head]] and [[Corpus:Neck|neck]], and it is part of the [[Corpus:Suprahyoid musculature|suprahyoid musculature]].<dcembed ratio="16x9"><dcEmbedUrl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/photos/43195-musculus-stylohyoideus"></dcEmbedUrl></dcembed> | ||
==Course== | ==Course== | ||
The stylohyoid muscle originates from the styloid process of the temporal bone and attaches to the body and | The stylohyoid muscle originates from the [[Corpus:Styloid process|styloid process]] of the [[Corpus:Temporal bone|temporal bone]] and attaches to the body and the greater horn (cornu majus) of the [[Corpus:Hyoid bone|hyoid bone]]. Some sources also describe attachment to the [[Corpus:Lesser horn|lesser horn]] (cornu minus). The attachment tendon of the stylohyoid muscle splits into two branches near its end, which encircle the intermediate tendon of the [[Corpus:Digastric muscle|digastric muscle.]]<dcembed><dcembedurlskatchfab src="https://sketchfab.com/3d-models/c5db65eafe0f4bd38d8ebba032b7104f" ui_controls="1"></dcembedurlskatchfab></dcembed> | ||
The attachment tendon splits into two | |||
<dcembed><dcembedurlskatchfab src="https://sketchfab.com/3d-models/c5db65eafe0f4bd38d8ebba032b7104f" ui_controls="1"></dcembedurlskatchfab></dcembed> | |||
==Innervation== | ==Innervation== | ||
The stylohyoid muscle is innervated by the facial nerve, which sends a stylohyoid | The stylohyoid muscle is innervated by the [[Corpus:Facial nerve|facial nerve]] (cranial nerve VII), which sends a stylohyoid branch to the muscle. | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
The stylohyoid muscle pulls the hyoid bone in a dorsal-cranial direction. Through the | The stylohyoid muscle pulls the hyoid bone in a backward and upward (dorsal-cranial) direction. Through the coordinated action of the [[Corpus:Suprahyoid muscle|suprahyoid]] and [[Corpus:Infrahyoid muscle|infrahyoid muscles]], the hyoid bone is positioned appropriately during activities such as swallowing, and the tension of the floor of the mouth is regulated. The stylohyoid muscle also plays a role in opening the jaw. | ||
<dcembed ratio="16x9"><dcembedurl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/videos/3580-musculus-stylohyoideus"></dcembedurl></dcembed> | <dcembed ratio="16x9"><dcembedurl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/videos/3580-musculus-stylohyoideus"></dcembedurl></dcembed> | ||
Version vom 4. August 2024, 13:37 Uhr
This text has been translated by an AI and may sound raw. It will be reviewed shortly. Thank you for your patience!
This text has been translated by an AI and may sound raw. It will be reviewed shortly. Thank you for your patience!
Definition
The stylohyoid muscle is a slender skeletal muscle located in the transition area between the head and neck, and it is part of the suprahyoid musculature.
Course
The stylohyoid muscle originates from the styloid process of the temporal bone and attaches to the body and the greater horn (cornu majus) of the hyoid bone. Some sources also describe attachment to the lesser horn (cornu minus). The attachment tendon of the stylohyoid muscle splits into two branches near its end, which encircle the intermediate tendon of the digastric muscle.
Innervation
The stylohyoid muscle is innervated by the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII), which sends a stylohyoid branch to the muscle.
Function
The stylohyoid muscle pulls the hyoid bone in a backward and upward (dorsal-cranial) direction. Through the coordinated action of the suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscles, the hyoid bone is positioned appropriately during activities such as swallowing, and the tension of the floor of the mouth is regulated. The stylohyoid muscle also plays a role in opening the jaw.