Corpus: Transverse colon
1. Definition
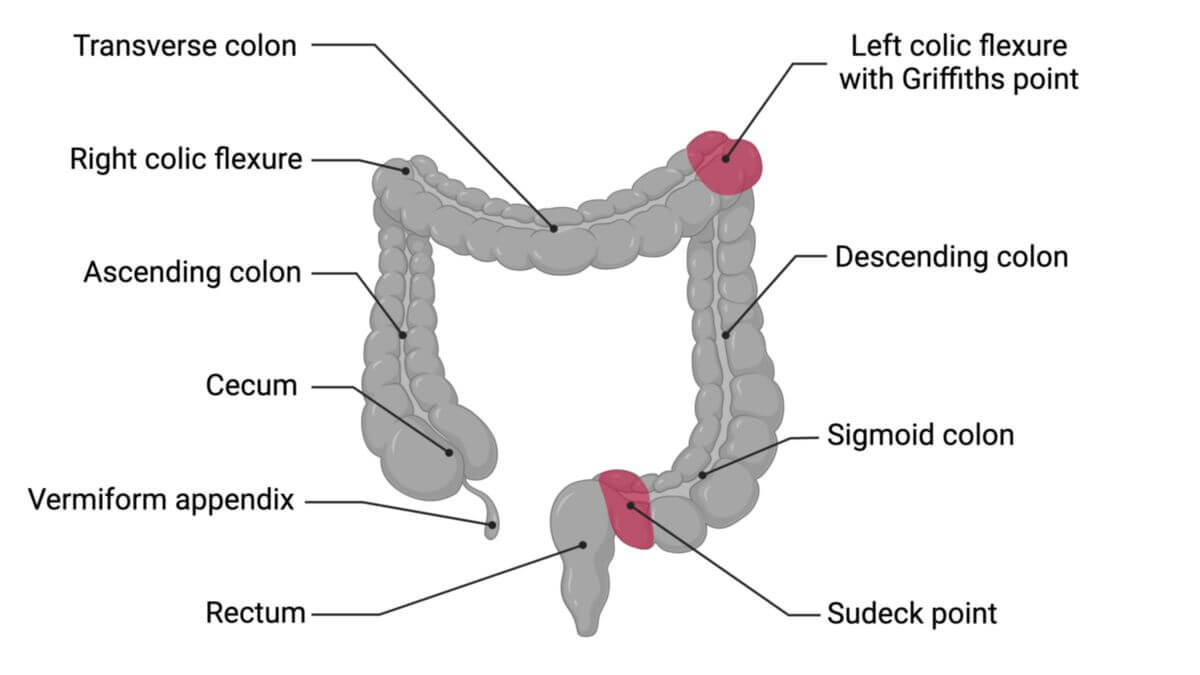
The transverse colon is the middle part of the colon, which lies between the right (flexura coli dextra) and left colonic flexure (flexura coli sinistra).
2. Anatomy
In contrast to the ascending and descending colon, the transverse colon lies intraperitoneally. Initially it runs ventrally from the colic impression of the liver, then in the upper abdomen from the right, where it touches the gallbladder, to the left cranially.
The left colonic flexure (flexura coli sinistra) is always higher than the right. It is attached to the diaphragm via the phrenicocolic ligament so that the left colonic flexure forms the base of the splenic niche. This is also where the transition to the following section of the intestine, the descending colon, is located. In addition, the transverse colon is flexibly suspended from a mesentery, the transverse mesocolon, and is characterised by semilunar folds of colon and haustra.
The Cannon-Böhm's point is located in the left third of the transverse colon.