Corpus: Scaphoid bone
Synonyms: scaphoid, navicular bone
1. Definition
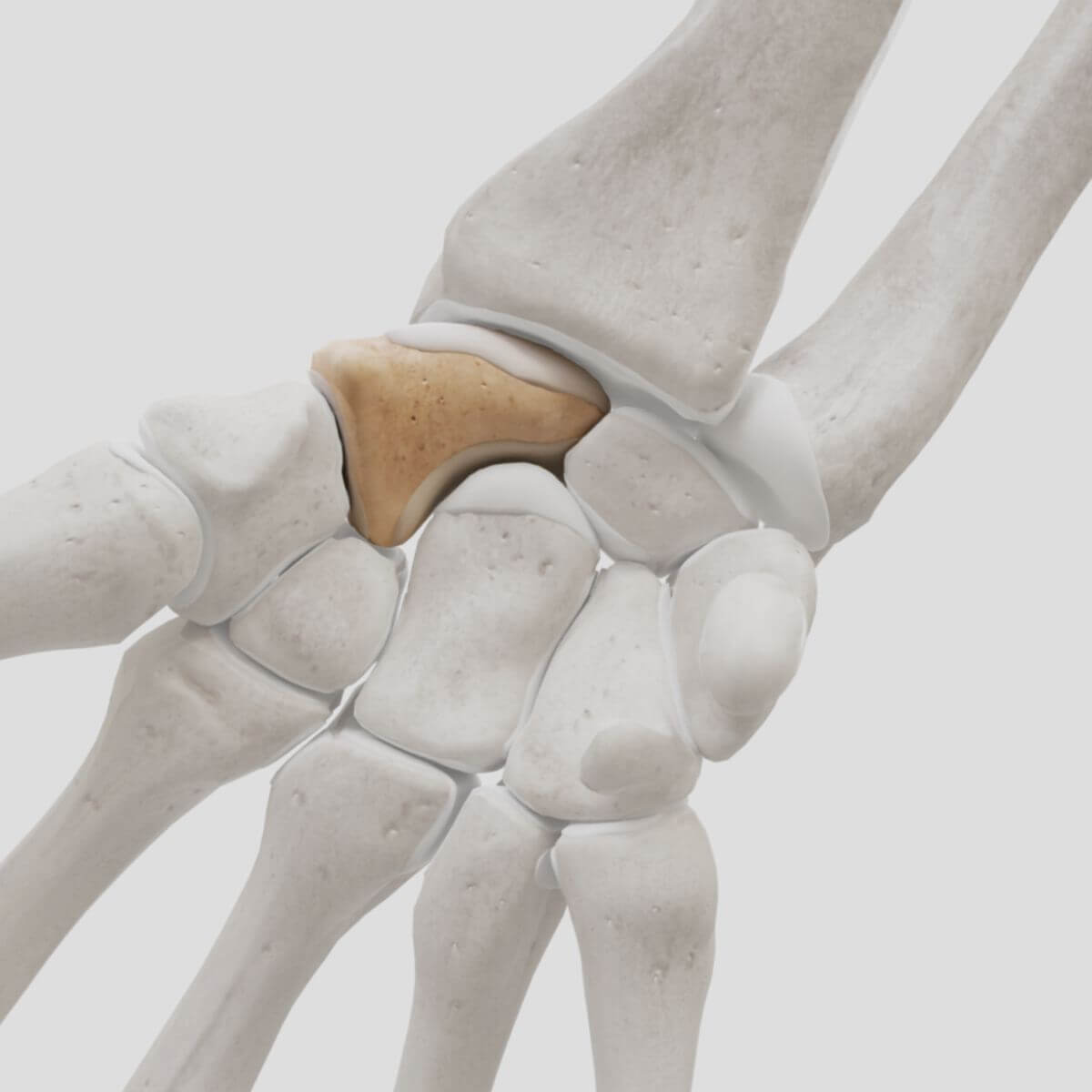
The scaphoid bone is the largest of the proximal carpal bones. Its name is derived from its boat-like shape.
2. Terminology
Partly due to the german term "Kahnbein," the scaphoid bone is often clinically equated with the navicular bone. However, according to the Nomina Anatomica Parisiensia, a clear distinction is made between the two bones.
3. Anatomy
The scaphoid bone is located on the radial side of the wrist (Carpus). It has 6 surfaces (facies). The superior surface of the scaphoid bone has a triangular outline and is convex and smooth. It articulates with the distal end of the radius. Ulnarly, the scaphoid bone connects with the lunate bone, and distally with the trapezium, trapezoid, and capitate bones. A ligamentous connection between the scaphoid and lunate bones is maintained via the scapholunate ligament. At the inferolateral angle of the scaphoid bone is the tubercle of the scaphoid bone, which serves as the origin for the abductor pollicis brevis muscle and the corpus:flexor retinaculum muscleflexor retinaculum muscle. During radial abduction of the hand, the scaphoid bone is the carpal bone that prominently protrudes on the palmar side of the hand.
3.1. Dimensions
The scaphoid bone has a length of approximately 16 mm and a width of about 28 mm. It is the largest of the four proximal carpal bones.
3.2. Ligaments
The scaphoid bone serves as the attachment or origin for various ligaments, including:
- :Scaphotrapezium ligament
- Scaphocapitate ligament
- Scapholunate ligament
- Scaphotrapeziotrapezoid ligament
3.3. Varieties
Varieties in the scaphoid bone that can lead to confusion in imaging include:
- Bipartite scaphoid bone
- Os centrale carpi
4. Clinic
Scaphoid fractures are the most common fractures of the carpal bones. Radiologically, during ulnar abduction, separation of the fracture pieces can be seen, whereas they are compressed during radial abduction. Both palmar and dorsal flexion open the fracture gap dorsally and palmarly, respectively. A disturbed fracture healing can lead to scaphoid nonunion, which in turn can lead to carpal instability, a condition known as SNAC-Wrist (scaphoid non-union advanced collapse).