Corpus: Lunate bone
1. Definition
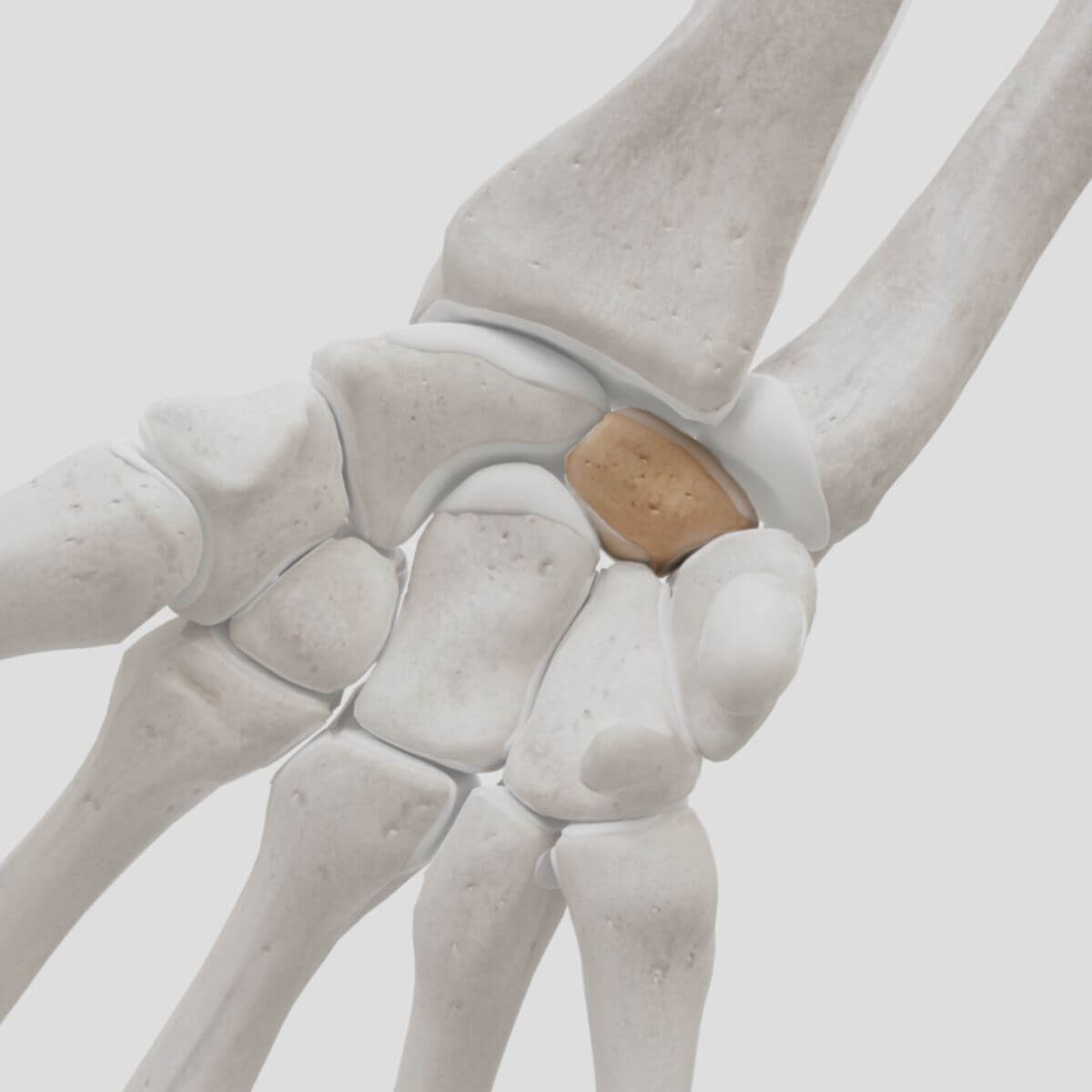
The lunate bone is a carpal bone of the proximal row. It owes its name to its roughly crescent-shaped form.
2. Anatomy
The lunate bone is located approximately in the middle of the carpus; it borders radially on the scaphoid bone and ulnarly on the triquetrum. It is in articular connection with both bones. Proximally, the lunate bone articulates with the distal surface of the radius and is thus involved in the radiocarpal articulation. Distally, the bone borders on the capitate bone and hamate bone and participates with them in the mediocarpal articulation.
2.1. Ligaments
The lunate bone serves as the insertion or origin of numerous ligaments of the wrist. These include:
3. Development
The bone core of the lunate bone develops between the 2nd and 5th year of life. It is ossified by the time the child reaches the age of 9.
4. Clinic
Trauma can cause injuries to the lunate bone, e.g. lunate dislocation or the rare lunate fracture. The most common disease of the lunate bone is lunate necrosis (Kienböck's disease).