Corpus: Semimembranosus muscle: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „==Definition== The '''semimembranosus muscle''' is a skeletal muscle that belongs to the flexors of thigh muscles.<dcembed ratio="16x9"><dcEmbedUrl src="https://www.doccheck.com/de/detail/photos/43029-musculus-semimembranosus"></dcEmbedUrl></dcembed> ==Course== ===Origin=== The semimembranosus muscle originates on the posterior surface of the ischial tuberosity, medial to th…“) |
K (Schützte „Corpus:Semimembranosus muscle“ ([Bearbeiten=Nur Administratoren erlauben] (unbeschränkt) [Verschieben=Nur Administratoren erlauben] (unbeschränkt))) |
(kein Unterschied)
| |
Aktuelle Version vom 17. Juni 2024, 15:04 Uhr
Definition
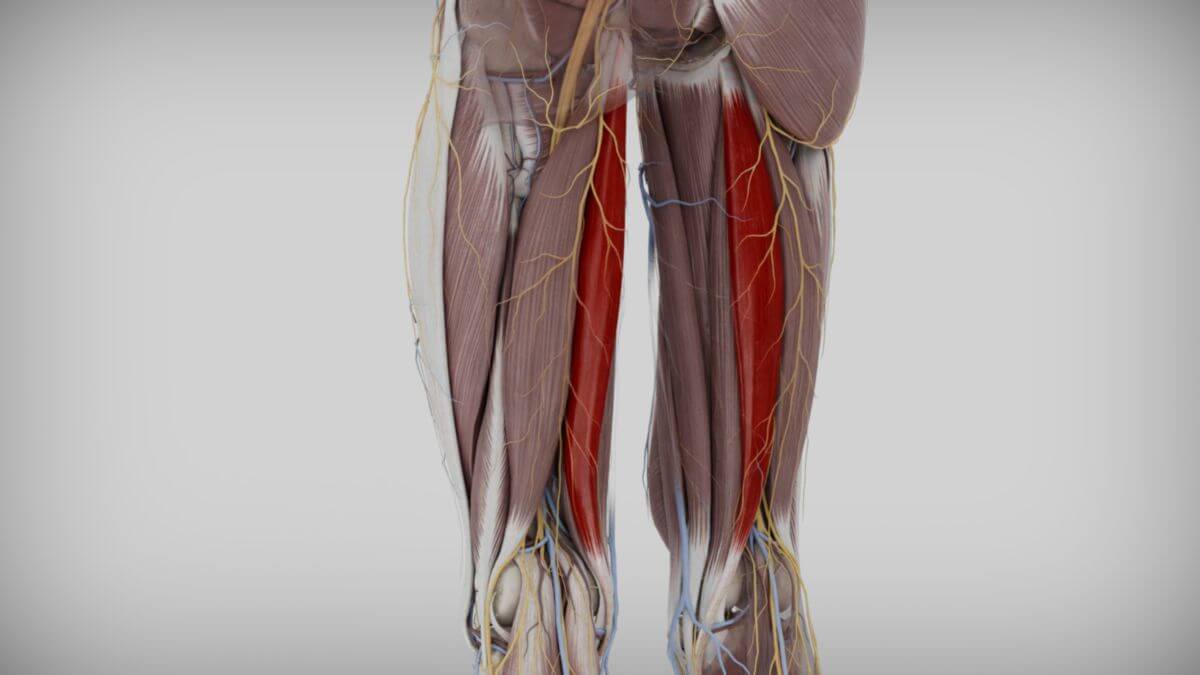
The semimembranosus muscle is a skeletal muscle that belongs to the flexors of thigh muscles.
Course
Origin
The semimembranosus muscle originates on the posterior surface of the ischial tuberosity, medial to the point of origin of the long head of the biceps femoris muscle.
Attachment
The attachment of the semimembranosus muscle is extensive and includes the medial condyle of the tibia, the fascia of the popliteus muscle, the oblique popliteal ligament, and the posterior side of the joint capsule of the knee. The semimembranosus bursa is located between the muscle insertion and the tibia.
Similar to the superficial pes anserinus formed by the insertion tendons of three muscles, the insertion of the semimembranosus muscle is also known as the deep pes anserinus.
Variety
In some cases, the muscle may be absent or form a unit with the semitendinosus muscle. The oblique popliteal ligament is also not always present.
Innervation
The semimembranosus muscle is innervated by the tibial nerve.
Arterial supply
The arterial supply is provided by the medial circumflex femoral artery, a branch of the deep femoris artery, and the popliteal artery.
Function
The semimembranosus muscle functions to flex the knee joint, extend the hip joint, and support the internal rotation of the tibia.