Corpus: Transverse part of nasalis muscle
from Latin: nasus - nose
Synonym: nasal muscle
1. Definition
2. Course
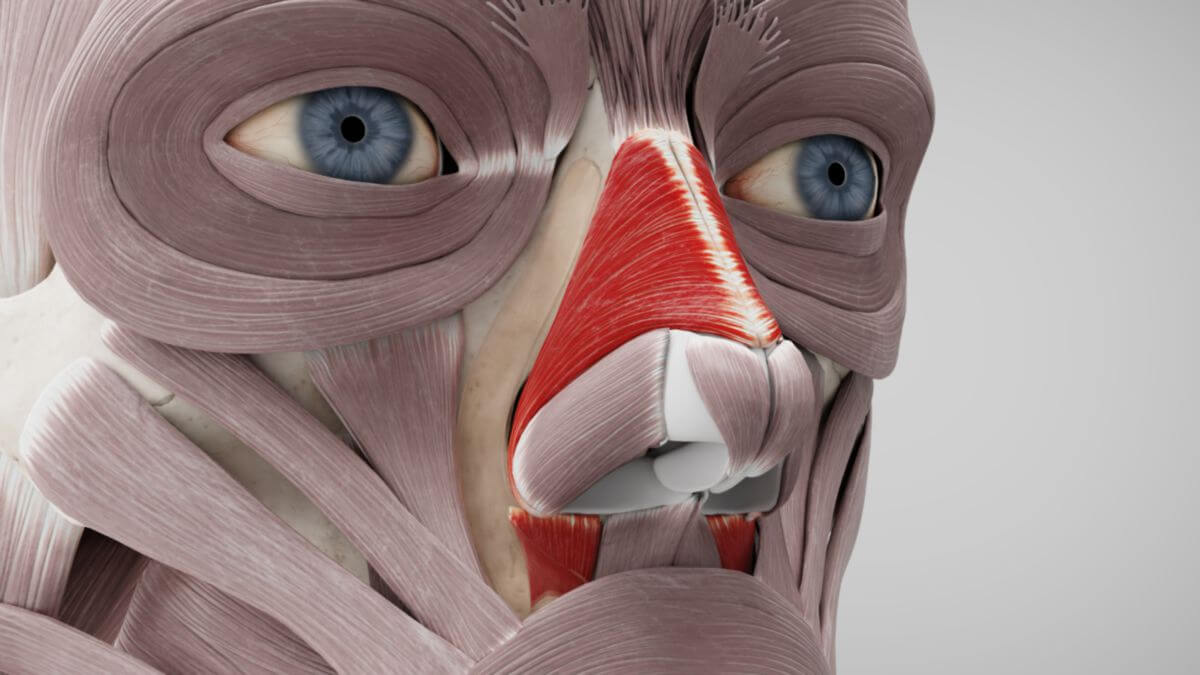
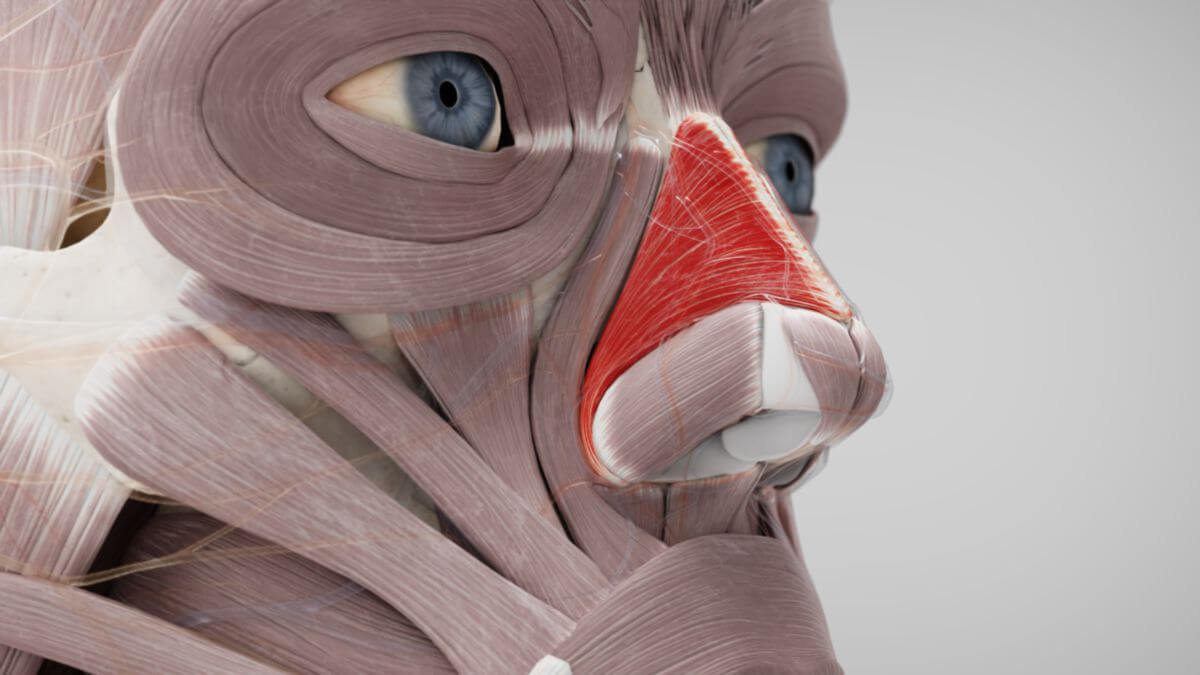
The nasalis muscle consists of two parts:
- Transverse part: It originates on the maxilla, above and slightly lateral to the incisive fossa. Its fibres run cranially and medially and insert on both sides into a thin aponeurosis that covers the nasal bridge. Some fibres radiate into the aponeurosis of the procerus muscle.
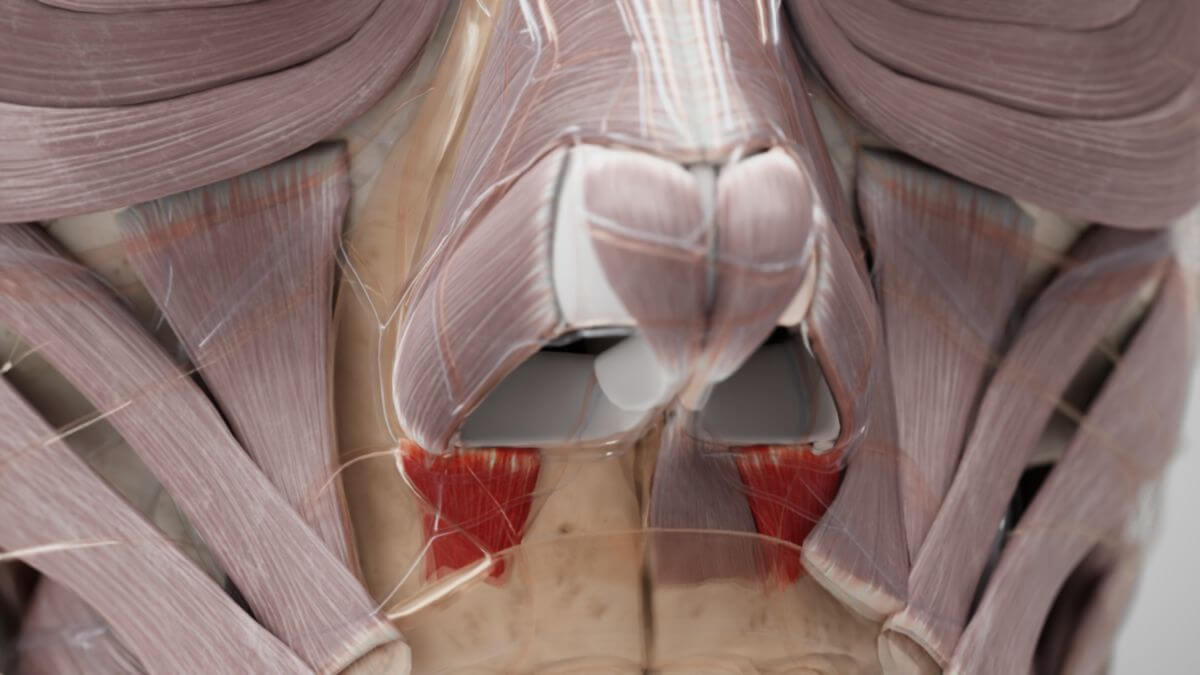
- Alar part: It originates in the incisive fossa of the maxilla – slightly medial and caudal to the origin of the transverse part - at the bony areas above the root of the 2nd incisor. From there the fibres run into the cartilage of the nasal wing (greater alar cartilage) and to the tip of the nose.
3. Innervation
The nasalis muscle is innervated by the rami buccales of the VII cranial nerve (facial nerve).
4. Function
The transverse part of the nasalis muscle pulls the nasal cartilage towards the maxilla, thereby narrowing the nostril. The alar part pulls the cartilage of the nostril laterally, thereby widening the nostril and facilitating nasal breathing.