Corpus: Semispinalis muscle
Achtung: Du siehst nicht die aktuelle, sondern eine ältere Version dieser Seite.
This text has been translated by an AI and may sound raw. It will be reviewed shortly. Thank you for your patience!
This text has been translated by an AI and may sound raw. It will be reviewed shortly. Thank you for your patience!
1. Definition
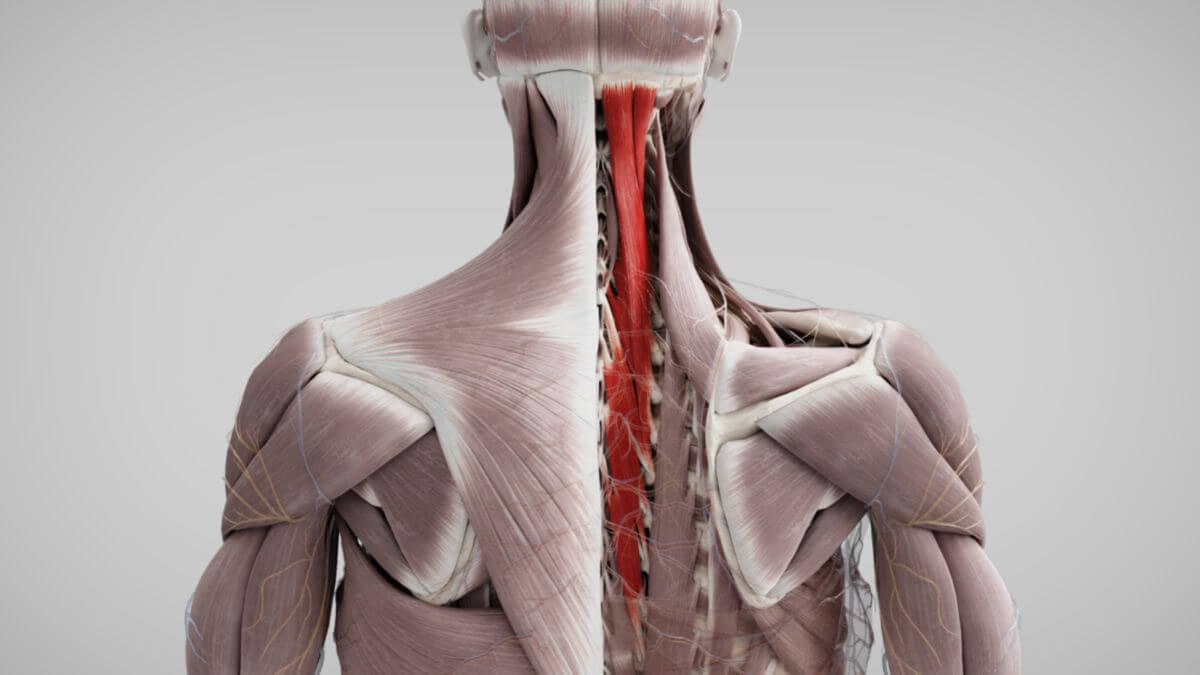
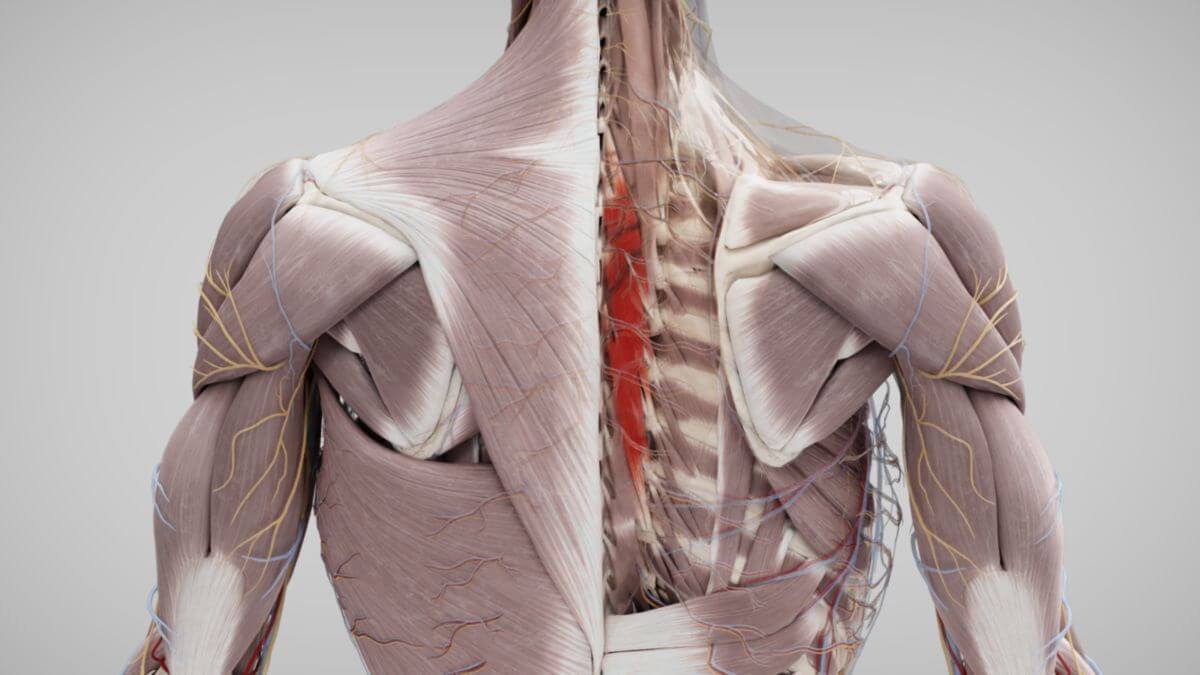
The Musculi semispinales are skeletal muscles of the back musculature. They belong to the medial tract of the erector spinae muscle.
2. Anatomy
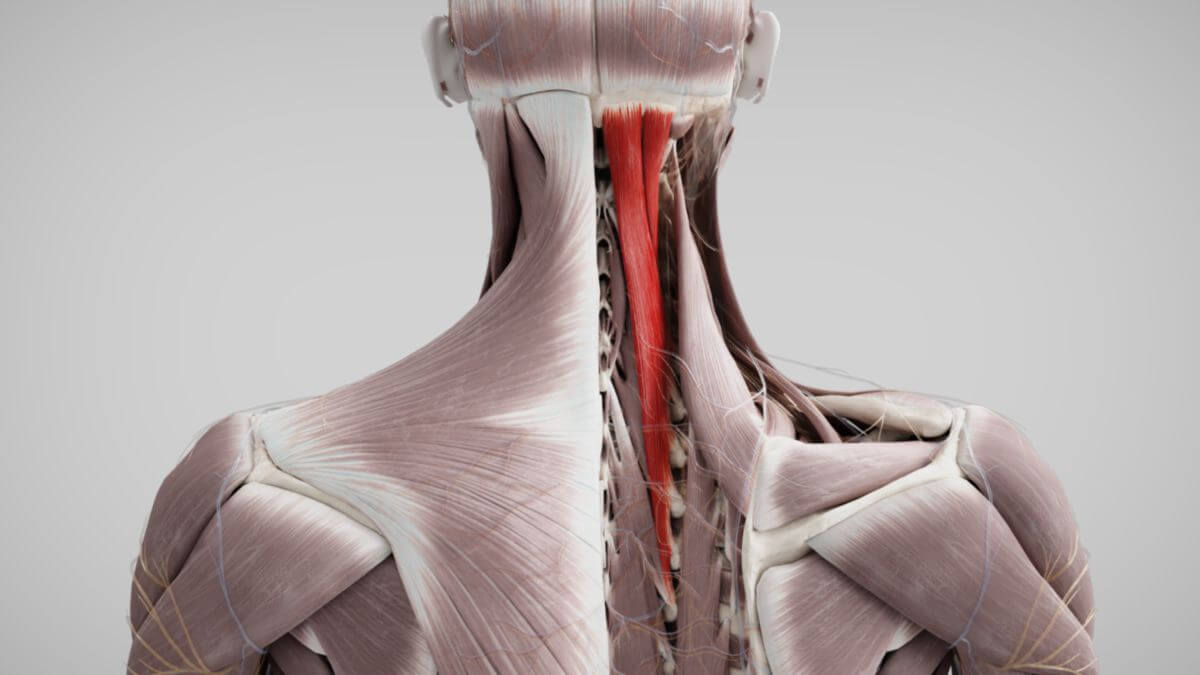
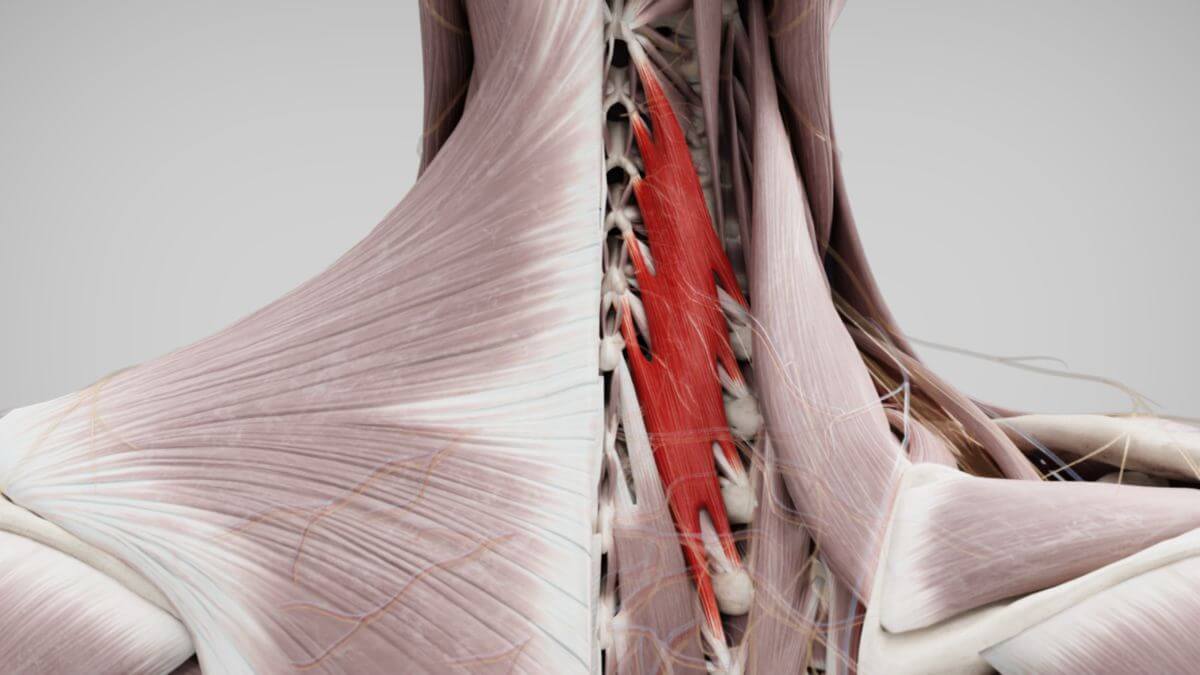
The semispinal muscles are located in the area of the head, cervical and thoracic spine. They originate from the processus transversus (or homologous areas) and usually attach 6 to 7 vertebral levels higher to the processus spinosus or occipital bone.
For better orientation, three muscle groups are distinguished:
- Musculus semispinalis capitis
- semispinalis cervicis muscle
- Musculus semispinalis thoracis
2.1. Musculus semispinalis capitis
The muscle tracts of the semispinalis capitis muscle originate from the articular processes of thoracic vertebra 6 to cervical vertebra 3. They attach in the medial area of the occipital bone between the superior and inferior nuchal lines.
2.2. Musculus semispinalis cervicis
The origins of the semispinalis cervicis muscle extend from thoracic vertebrae 7 - 2, the corresponding insertions extend from cervical vertebrae 6 - 2.
2.3. Musculus semispinalis thoracis
The areas of origin of the semispinalis thoracis muscle lie on the transverse processes of thoracic vertebrae 12 - 7. The corresponding insertion areas extend from the 4th thoracic vertebra to the 6th cervical vertebra.
3. Innervation
The semispinalis muscles are innervated by the medial branches of the posterior rami from the respective segmental spinal nerves. The semispinalis capitis muscle is occasionally joined by lateral branches of the posterior rami.
4. Function
The semispinalis capitis muscle turns the head to the opposite side when contracted on one side. When contracted on both sides, the head is dorsiflexed (stretched).
When contracted on one side, the semispinalis cervicis and thoracis muscles rotate the respective area of the spine to the opposite side, resulting in lateral flexion to the same side. When contracted on both sides, they contribute to the extension.