Corpus: Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(Englische Seite angelegt) |
K (Schützte „Corpus:Middle pharyingeal constrictor muscle“ ([Bearbeiten=Nur Administratoren erlauben] (unbeschränkt) [Verschieben=Nur Administratoren erlauben] (unbeschränkt))) |
(kein Unterschied)
| |
Version vom 21. Juli 2024, 21:12 Uhr
This text has been translated by an AI and may sound raw. It will be reviewed shortly. Thank you for your patience!
This text has been translated by an AI and may sound raw. It will be reviewed shortly. Thank you for your patience!
from Latin: constringere - to constrict and Greek: pharynx - throat
Definition
The Musculus constrictor pharyngis medius is a striated skeletal muscle and the middle of the three constrictors of the pharyngeal musculature. It is joined cranially by the constrictor pharyngis superior muscle and caudally by the constrictor pharyngis inferior muscle.
Embryology
The musculus constrictor pharyngis medius forms predominantly from the muscle anlage of the 4th gill arch.
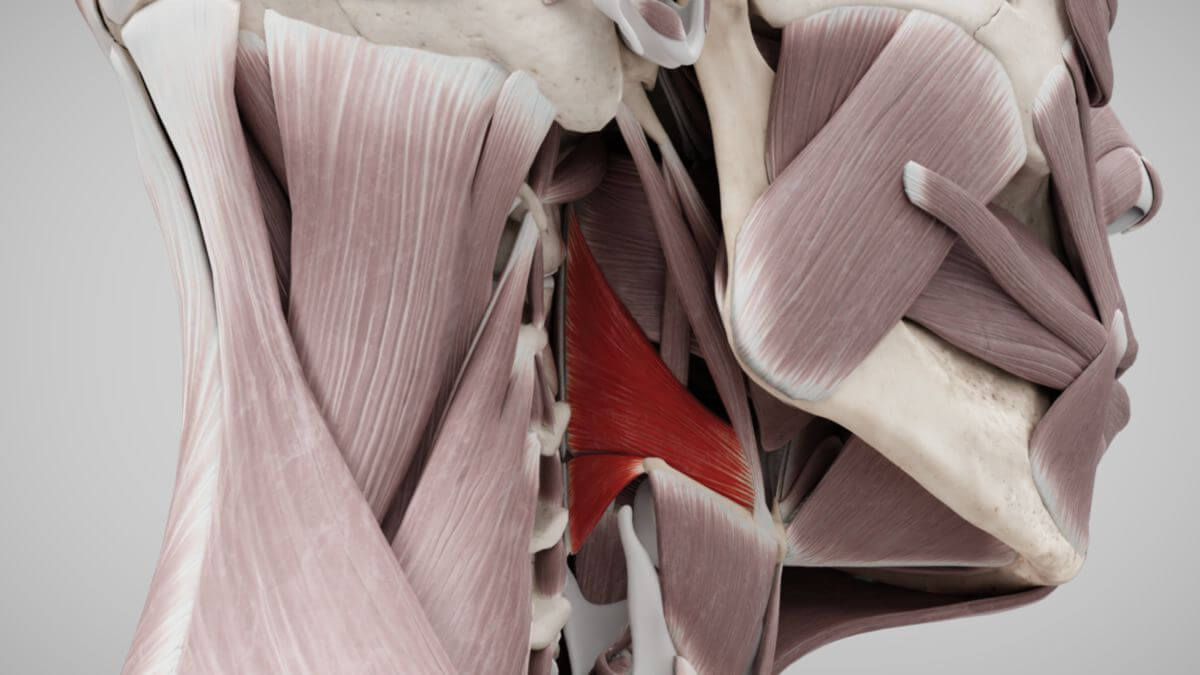
Anatomy
Classification
The constrictor pharyngis medius muscle consists of two parts:
- Pars chondropharyngea
- Pars ceratopharyngea
Origin
The pars chondropharyngea has its origin at the small horn (cornu minus) of the hyoid bone (os hyoideum), the pars ceratopharyngea at the large horn of the hyoid bone (cornu majus).
Attachment
The fibres of the constrictor pharyngis medius muscle extend obliquely cranially, medially and dorsally and connect with the fibres of the muscle on the opposite side in the pharyngeal raphe. They overlap the caudal fibres of the constrictor pharyngis superior muscle like a roof tile.
Innervation
The constrictor pharyngis medius muscle is innervated by the pharyngeal plexus, a nerve plexus consisting of the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX nerve) and the vagus nerve (X nerve).
Function
Swallowing
The contraction of the constrictor pharyngis medius muscle constricts the pars oralis pharyngis (oropharynx) and pushes the food bolus towards the oesophagus during swallowing.
Phonetics
The constrictor pharyngis medius muscle is involved in the formation of pharyngeal sounds - especially laterally, with assumed involvement of the constrictor pharyngis inferior muscle - and low, posterior vowels (e.g. "a").