Corpus: Spermatic cord
1. Definition
The term spermatic cord refers to the approximately 20 cm long bundle of vessels, nerves and the spermatic duct that runs through the inguinal canal in men.
2. Anatomy
2.1. Wall structure
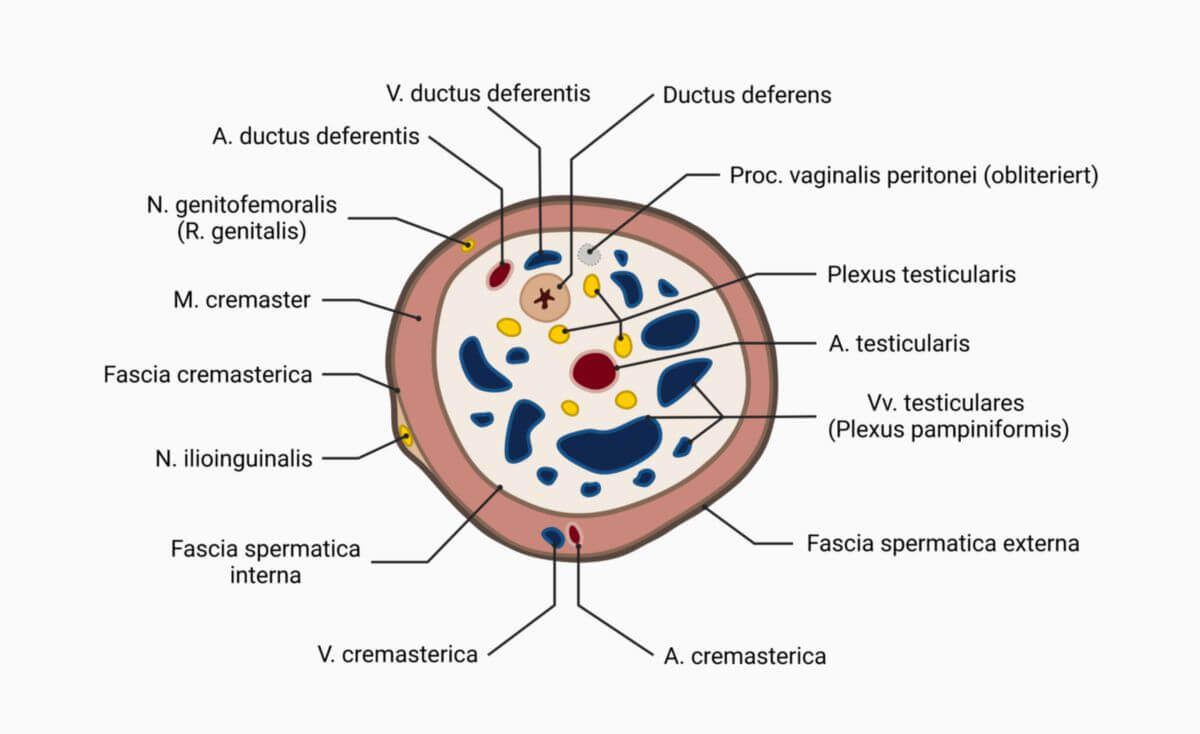
The spermatic cord is enclosed by several layers of different tissues, all of which have a corresponding abdominal wall due to the descent of testis:
- dartos fascia ("flesh skin") - subcutaneous fatty tissue
- external spermatic fascia - Scarpa's fascia
- cremasteric fascia - fascia of the obliquus internus abdominis muscle
- cremaster muscle - separation of the obliquus internus abdominis muscle (partly also of the transversus abdominis muscle)
- internal spermatic fascia - transverse fascia
- tunica vanginalis - vaginal process (funnel-shaped protrusion of the peritoneum)
2.2. Contained structures
In addition, the spermatic cord contains the following structures:
- Spermatic duct
- Blood vessels
- Nerves
- genitofemoral nerve
- Plexus testicularis
- plexus of ductus deferens
- ilioinguinal nerve (runs outside the spermatic cord between the cremasteric fascia and the external spermatic fascia)
- lymphatic vessels
- vaginal process