Corpus: Chest tube
Synonyms: chest drainage, thorax drainage, thoracic drainage
1. Definition
The term chest tube refers to a drainage system used to remove fluids and/or air from the chest (thorax), pleural cavity, or mediastinum.
2. Classification
2.1. ...by body cavity
The classification is based on the space from which fluid or air is being drained:
- Pleural drainage: Drains fluid or air from the pleural cavity
- Mediastinal drainage: Drains blood and serum after cardiac surgery
- Pericardial drainage: Drains excess fluid from the pericardial sac
In clinical practice, the term "thoracic drainage" usually refers to pleural drainage.
2.2. ...by insertion site
Pleural drainages are classified based on their placement:
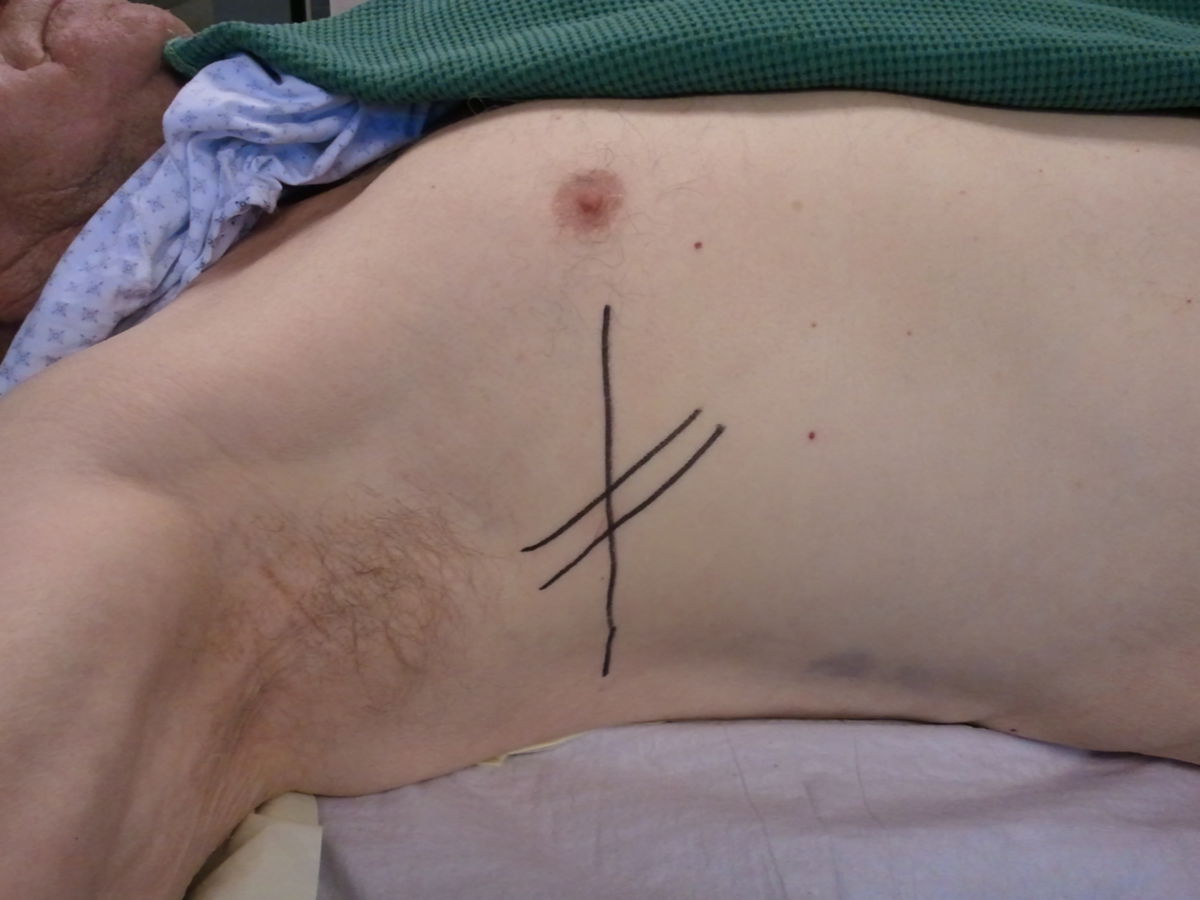
- Bülau drainage: Inserted at the 4th intercostal space (ICS) between the anterior and mid-axillary line; this is the standard approach.
- Monaldi drainage: Inserted at the 2nd intercostal space along the midclavicular line; used only in specific cases.
2.3. ...by system structure
- Single-chamber system: An outdated design consisting of a single bottle partially filled with liquid, into which the drainage tube is submerged.
- Two-chamber system: Includes a surge chamber and a separate collection chamber for fluid drainage.
- Three-chamber system: Adds a third chamber functioning as a safety valve to regulate suction if it is not otherwise adjustable.
- Four-chamber system: Similar to the three-chamber system, with an additional chamber to monitor pressure changes in the pleural space.
Electronic chest drainage systems use an electronically controlled suction mechanism that generates a vacuum and collects secretions in a canister. The vacuum level can be individually adjusted for each patient, and suction is only actively applied if the actual and target pressure values differ.
3. Indication
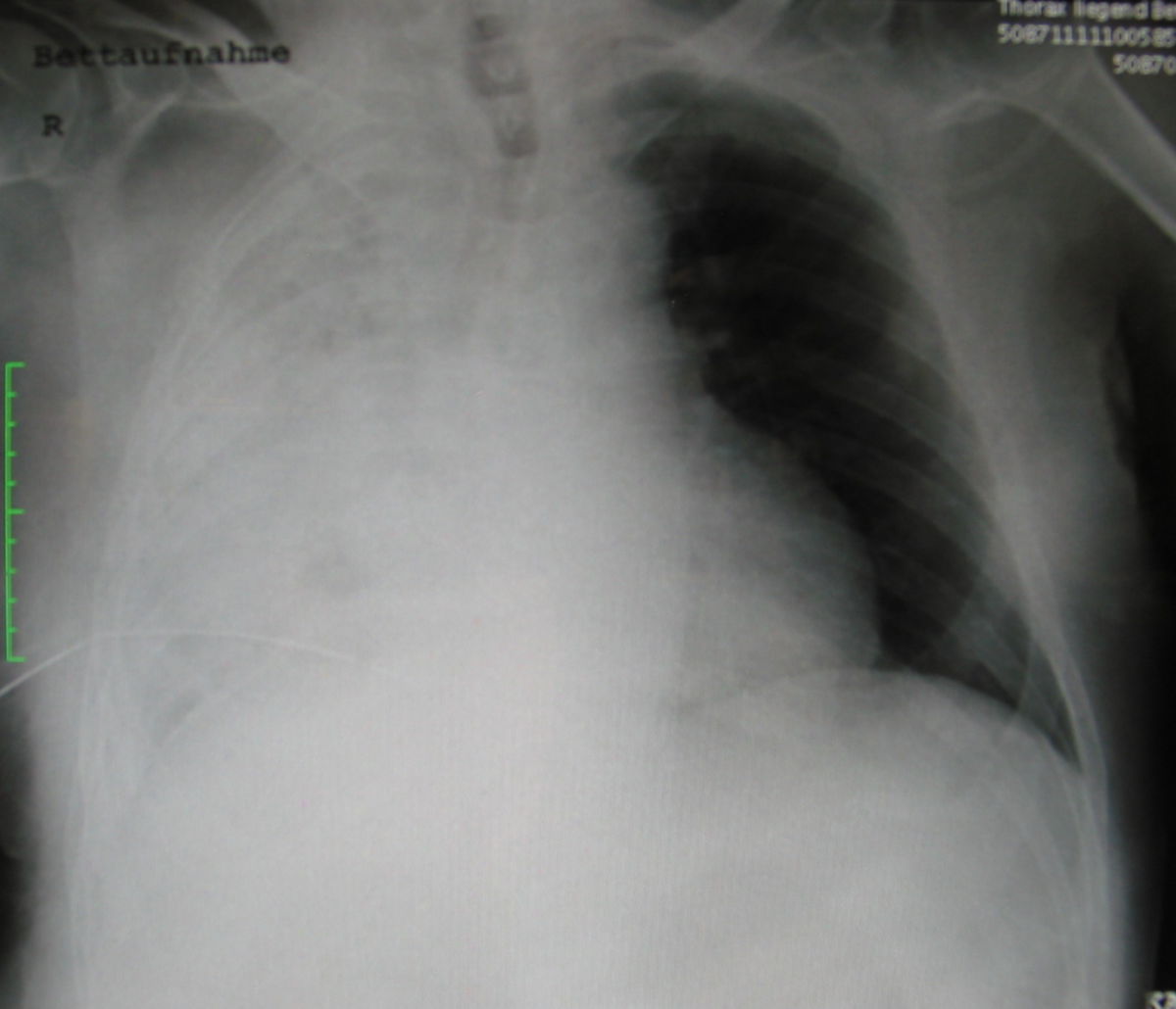
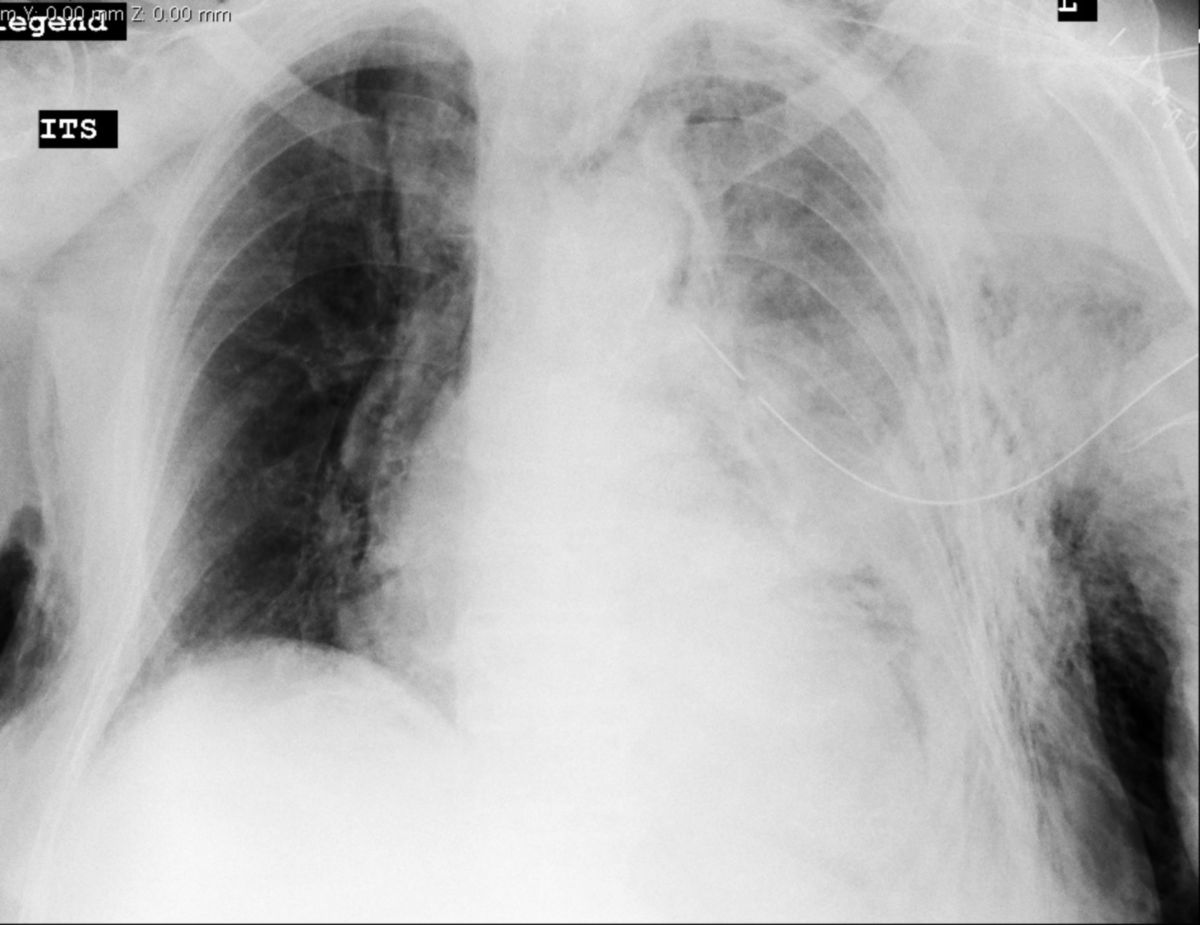
- Pneumothorax, especially tension pneumothorax (emergency indication)
- Hemothorax
- Serous pleural effusion (e.g., recurrent, parapneumonic, or malignant effusion)
- Chylothorax
- Pleural empyema
- Recurrent hepatic hydrothorax
- Subcutaneous emphysema
- Multiple rib fractures
- Postoperative management (e.g., after thoracotomy or sternotomy)
- Drug administration (e.g., pleurodesis)
4. Contraindication
Relative contraindications for chest tube placement include:
- Increased bleeding tendency (e.g., due to anticoagulation)
- Pleural adhesions (e.g., following pleurodesis or lung surgery)