Corpus: Brachiocephalic trunk
From Latin: "truncus" - trunk, "brachium" - arm, and from Greek: "cephalon" - head.
Synonyms: Arm-Head Trunk, Anomalous Artery, Innominate Artery, Brachiocephalic Artery.
1. Definition
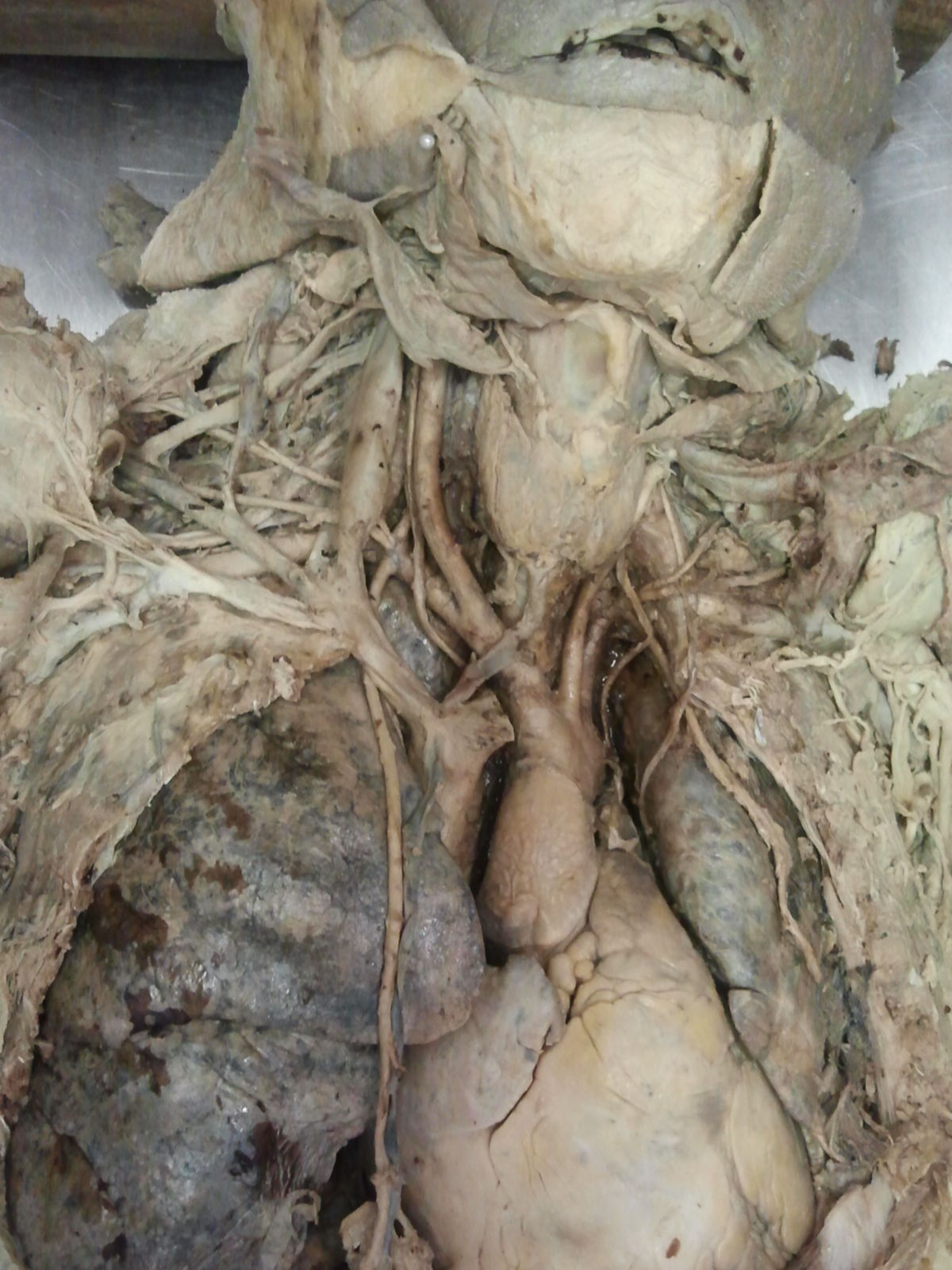
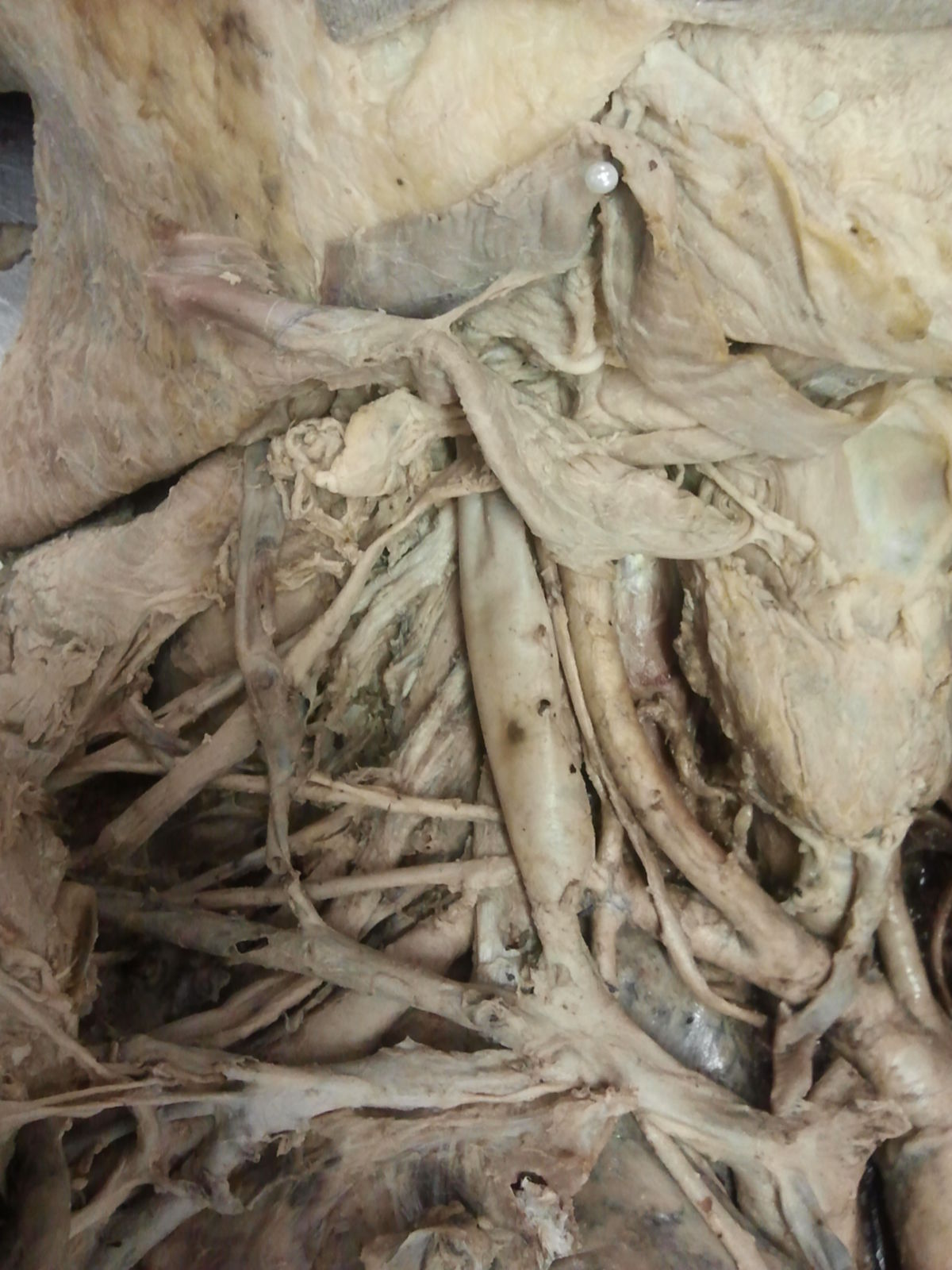
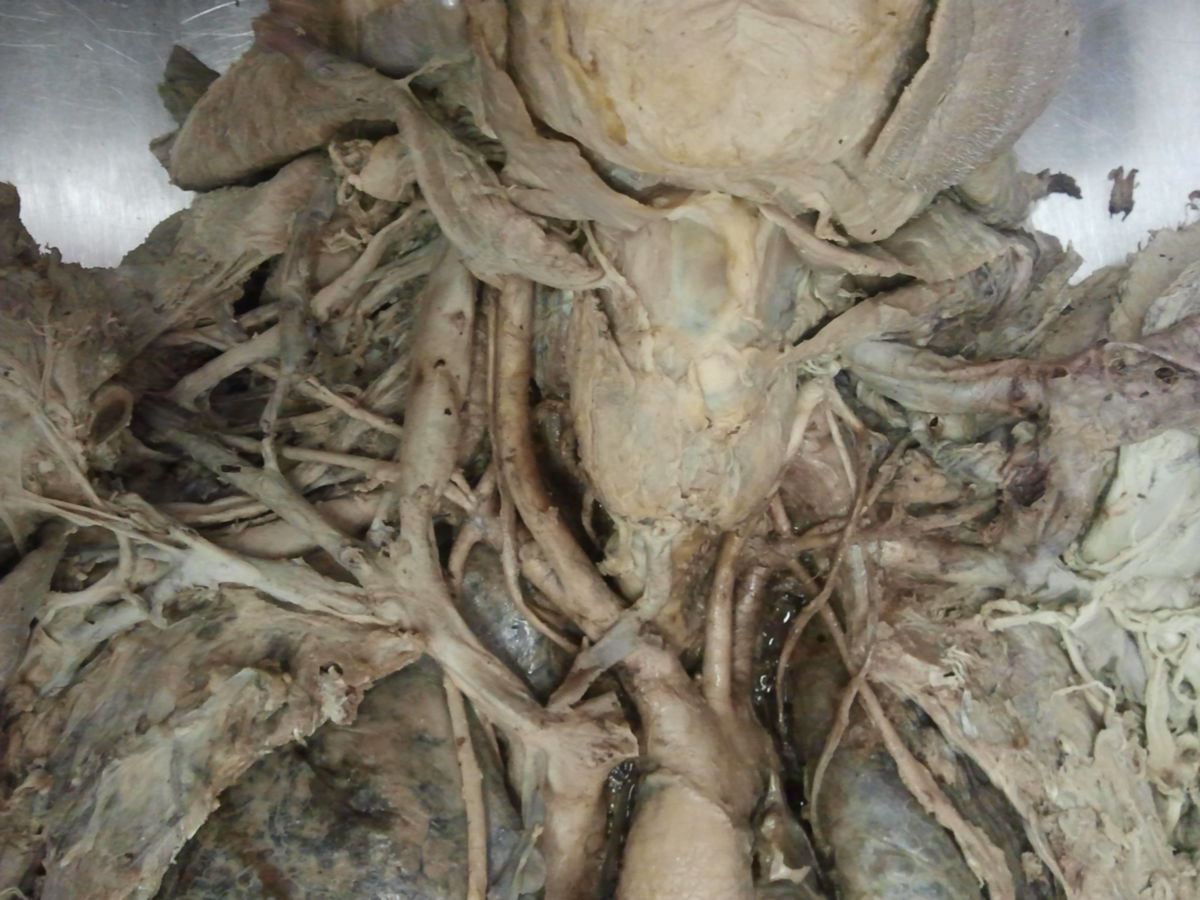
The brachiocephalic trunk is the first major arterial branch from the aorta. Historically, it has also been referred to as the "anomalous artery" or "innominate artery."
2. Course
The brachiocephalic trunk is typically found only on the right side of the body in most individuals. It arises from the arch of the aorta and serves as the common vessel trunk for the right subclavian artery and the right common carotid artery. On the left side, these vessels usually originate separately from the aortic arch. As a variation, the left common carotid artery can also originate from the brachiocephalic trunk in some cases.
3. Topography
The brachiocephalic trunk is adjacent to the following anatomical structures:
- Anteriorly: Left brachiocephalic vein and manubrium of the sternum
- Posteriorly: Trachea and vagus nerve
- Posteriorly and to the left: Left common carotid artery
- To the right: Right brachiocephalic vein
4. Branches
Typically, the brachiocephalic trunk does not emit its own branches; however, as a variation, a small branch may exist serving the lower part of the thyroid gland, known as the thyroid ima artery. This artery can be injured during a tracheotomy (incision into the trachea), leading to potentially life-threatening bleeding.
5. Function
The brachiocephalic trunk supplies arterial blood to the right arm and the right side of the head, neck, and brain.